Introduction
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic and progressive condition characterised by the fibrosis of the liver tissue which results from long-term liver damage and inflammation.
The liver plays a vital role in various physiological processes, including detoxification, metabolism of nutrients, synthesis of proteins, and storage of glycogen and vitamins. When cirrhosis develops, these essential functions are compromised leading to serious complications.
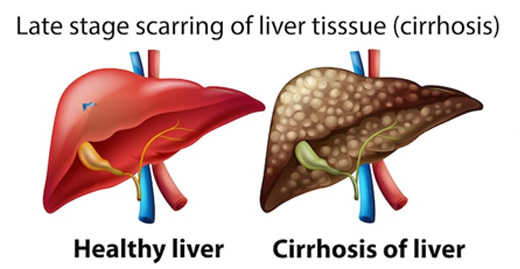
Understanding Liver Cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis entails the gradual replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, impairing liver function over time. Manifestations of cirrhosis include fatigue, jaundice, abdominal discomfort, ascites, edema, easy bruising, itching, spider angiomas, gastrointestinal disturbances, cognitive changes, weight loss, and increased infection susceptibility. Complications, ranging from varices to hepatocellular carcinoma, further exacerbate the condition's severity.
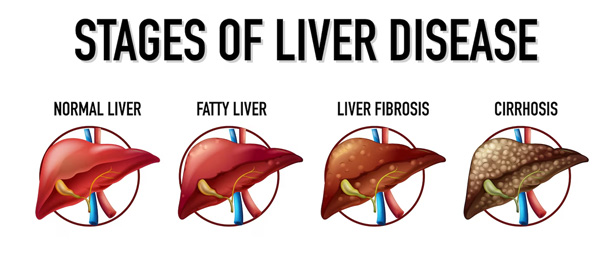
Causes of Liver Cirrhosis

Chronic Alcoholism
Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis.
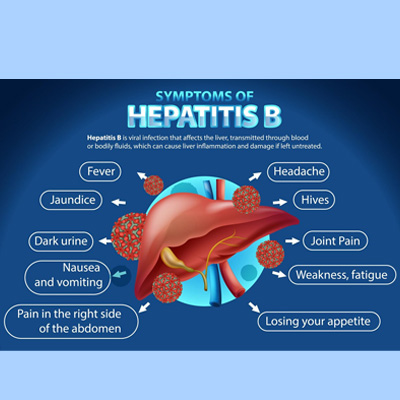
Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) can lead to liver inflammation and progressive liver damage, eventually causing cirrhosis.
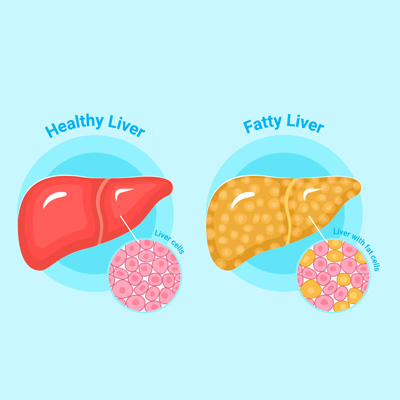

Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH):
NAFLD and NASH are conditions characterised by the accumulation of fat in the liver (steatosis). Over time, inflammation and liver cell injury can occur, leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. These conditions are often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
Autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis (formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis), and primary sclerosing cholangitis are autoimmune diseases that can cause inflammation and damage to the liver, leading to cirrhosis.
Genetic Disorders
Genetic conditions such as hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can lead to abnormal accumulation of substances in the liver, causing liver damage and cirrhosis.
Chronic Biliary Obstruction
Conditions that cause chronic obstruction of the bile ducts, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis, can lead to bile accumulation, liver inflammation, and eventually cirrhosis.
Signs and symptoms

Fatigue
Persistent tiredness, lack of energy are common symptoms of liver cirrhosis, often affecting daily activities .
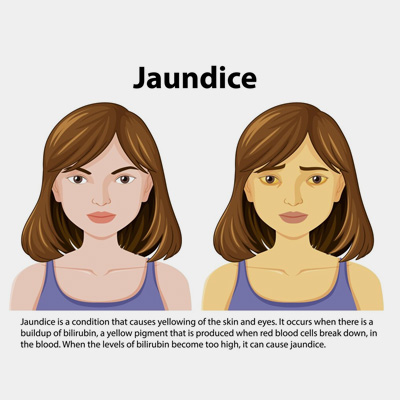
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by the buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment, in the bloodstream. It occurs when the liver is unable to effectively process bilirubin, leading to its accumulation in the body.

Abdominal Pain or Discomfort:
Some individuals may experience abdominal pain or discomfort, often in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, where the liver is located.
Edema
Edema is the buildup of fluid in the body's tissues, leading to swelling, particularly in the legs, ankles, and feet.
Easy Bruising or Bleeding
Liver cirrhosis can lead to decreased production of clotting factors and platelets, increasing the risk of easy bruising and bleeding, such as nosebleeds or bleeding gums.

Itchy Skin
Some individuals with cirrhosis may experience persistent itching , which can be attributed to the buildup of bile salts in the bloodstream due to impaired liver function.

Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Liver cirrhosis can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, or constipation.

Changes in Mental Function
Advanced liver cirrhosis can lead to cognitive changes, confusion, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems, collectively known as hepatic encephalopathy.

Weight Loss and Loss of Appetite
Some individuals with cirrhosis may experience unintentional weight loss and a reduced appetite .
Ascites
Ascites is the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, leading to abdominal swelling. It occurs due to increased pressure in the veins of the liver (portal hypertension), which causes fluid to leak into the abdomen.
Spider Angiomas
Spider angiomas are small, spider-like blood vessels that may appear on the skin, particularly on the chest, shoulders, and face. They are caused by increased pressure in the blood vessels of the skin.
Increased Susceptibility to Infections
Liver cirrhosis can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including respiratory infections, urinary tract infections.
Complications
- Varices
Due to portal hypertension , veins gets dilated leading to varices e.g esophageal , gastric varices which can lead to severe bleeding
- Hepatic Encephalopathy
Buildup of toxins in the bloodstream, such as ammonia, due to impaired liver function. Hepatic encephalopathy can lead to cognitive changes, confusion, altered consciousness, and coma.
- Hepatorenal Syndrome
Progressive kidney dysfunction secondary to liver cirrhosis, characterised by decreased kidney function, low urine output, and electrolyte imbalances.
- Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
A condition characterised by abnormal widening of the blood vessels in the lungs due to liver dysfunction which can lead to shortness of breath, hypoxemia (low oxygen levels), and difficulty breathing, particularly with exertion.
- Malnutrition
Liver cirrhosis can impair the absorption and metabolism of nutrients, leading to malnutrition, weight loss, and muscle wasting.
- Hormonal Imbalances
Liver cirrhosis can affect hormone production, leading to hormonal imbalances, including hypogonadism (reduced sex hormone production), gynecomastia (enlargement of breast tissue in men), and menstrual irregularities in women.
- Bone Disorders
Liver cirrhosis can lead to bone disorders such as osteoporosis (weak, brittle bones) and osteomalacia (softening of bones), due to impaired vitamin D metabolism and decreased bone density.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
Liver cirrhosis can disrupt fluid and electrolyte balance in the body, leading hyponatremia (low sodium levels), hyperkalemia (high potassium levels), and alkalosis or acidosis
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Liver cirrhosis is a significant risk factor for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer
Diagnosis
- Liver Function tests
to assess levels of liver enzymes like ALT , AST.Abnormal LFT results can indicate liver damage or dysfunction.
- Complete Blood Count
A blood test to assess for anaemia, thrombocytopenia , and other blood abnormalities.
- Coagulation Studies
Tests to assess blood clotting function, including prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT).
- Autoimmune Markers
Blood tests to detect autoimmune markers associated with autoimmune liver diseases, such as autoimmune hepatitis or primary biliary cholangitis.
- USG
to assess liver size, texture, and blood flow, as well as detect the presence of liver nodules, ascites.
- CT Scan or MRI
to detect liver lesions, assess portal hypertension
- FibroScan
A non-invasive imaging technique that measures liver stiffness, which can help assess the degree of liver cirrhosis.
Homoeopathy and Liver Cirrhosis
Homoeopathy offers a holistic approach to liver cirrhosis management, aiming to address underlying imbalances and promote self-healing. Several homoeopathic remedies show promise in alleviating cirrhosis symptoms and supporting liver function.
Homoeopathic medicines for liver cirrhosis
- Carduus Marianus
- Pain in region of liver
- There is sensation of fullness and soreness with moist skin
- Constipation with stools hard , knotty alternates with diarrhoea
- Stools are bright yellow
- Hyperaemia of liver with jaundice
- Cirrhosis with dropsy
- Appetite reduced , nausea , retching , vomiting of green , acid fluid
- Lycopodium
- It is useful remedy with weak digestive system where the functions of liver is seriously disturbed
- Skin shows yellowish spots
- Bloating of abdomen after a light meal
- Liver is sensitive
- Brown spots on abdomen
- Dropsy due to hepatic disease
- Pain shooting across lower abdomen from right to left
- Stools are hard , small and difficult and incomplete
- Phosphorus
- Weak , empty all gone sensation felt in abdomen
- Liver gets congested
- Acute hepatitis
- Jaundice
- Large yellow spots on abdomen
- Vomiting , water is thrown up as soon as it gets warm in stomach
- Stools are long , narrow, hard like a dog’s stools
- Painless , copious debilitating diarrhea with green mucus like sago
- Great weakness after stools
- Wounds bleed easily
- Petechiae , ecchymosis
- Nux Vomica
- Abdominal colic with flatulent distention
- Liver engorged, with stitches and soreness
- Sour taste and nausea in the morning after eating
- Epigastric region bloated with pressure as of a stone after eating
- Wants to vomit but cannot
- Constipation with frequent urging, feeling as if some part remained unexpelled
- Patient suffers from alternate diarrhoea and constipation
- Diarrhoea with jaundice
- Arsenic Album
- Patient gets exhausted after slightest exertion
- Pain in abdomen like gnawing, burning pains like coals of fire relieved by heat
- Liver and spleen painful and enlarged
- Ascites and anasarca
- Abdomen is swollen and painful
- Cannot bear the sight and smell of food
- Nausea , retching and vomiting , after eating and drinking
Benefits of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Individualised Care: Homoeopathy recognizes that each person is unique. A homoeopath will assess your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle to prescribe a personalised treatment plan tailored to your needs.
- Gentle and Natural: Homoeopathic remedies are derived from natural substances and are known for their minimal side effects. They work in harmony with the body, promoting self-healing and overall well-being.
- Holistic Approach: Homoeopathy takes into account not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and mental aspects of an individual. It aims to restore balance at all levels, providing comprehensive care.
- Long-Term Relief: By addressing the underlying causes of Ulcerative Colitis,homoeopathy strives to achieve long-term relief and improved quality of life.
Patient Review
Consulting a Homeopath
Individualised treatment is paramount in Sanjivani homoeopathy, emphasising detailed case analysis and personalised remedies. Consulting a qualified Sanjivani homoeopath allows for tailored treatment plans, incorporating dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and specific remedies to address liver cirrhosis comprehensively. Regular monitoring and adjustments ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes and long-term benefits.
Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic USP
- No homoeopathy Dietary Restrictions:
Allows patients to enjoy foods like onion, garlic, and coffee, ensuring a stress-free treatment journey.
- 24/7 Online Consultations:
Enables convenient access to doctors with detailed counseling, history management, and follow-ups.
- Highly Skilled Team:
Experienced BHMS and MD doctors, supported by multilingual and professional staff.
- Patient-Centric Care:
Simplifies treatment with modern, adaptable solutions and clear communication.
Click Here for Detailed "Sanjivani USP"
FAQ's
- What is homoeopathy ?
Homoeopathy is a holistic science which belives in the law of Similia Similibus Curenter i.e Like Cures Like .It was discovered by Dr Samuel Christian Hahnemannn in 1796.
- Is there any side effects of homoeopathy?
As homoeopathic medicines are made from natural substances this medicines have no side effects and are completely safe to consume
- Is there any diet restriction to take homoeopathic medicines?
There are no diet restrictions for homoeopathic medicines. One should only avoid eating or drinking any liquid other than water at least 30 minutes before and after taking homoeopathic medicines.
Click Here for "Frequently Asked Questions."
Conclusion
Sanjivani Homeopathy presents a promising adjunctive therapy for managing liver cirrhosis, offering a holistic approach to symptom relief and liver support. While conventional treatments focus on symptom management, Sanjivani homoeopathy addresses the underlying imbalances contributing to cirrhosis progression. Consulting a qualified Sanjivani homoeopath enables personalised treatment plans, integrating dietary and lifestyle modifications with targeted remedies. By prioritising individualised care and holistic healing, Sanjivani homoeopathy plays a valuable role in optimising liver cirrhosis management and improving patient outcomes.
Disclaimer : The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any treatment for Liver Cirrhosis or any other medical condition.


