Introduction
A goitre is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck just below Adam's apple. Although goitres are usually painless, a large goitre can cause a cough and make it difficult for them to swallow or breathe.Thyroid is a gland found in the neck just below Adam’s apple. It secretes hormones that help regulate bodily functions, including metabolism, the process that turns food into energy. It also regulates heart rate, respiration, digestion, and mood.A condition that increases the size of thyroid is called a goitre. A goitre may develop in anyone, but is more common in women. Sometimes, it affects the way the thyroid functions.
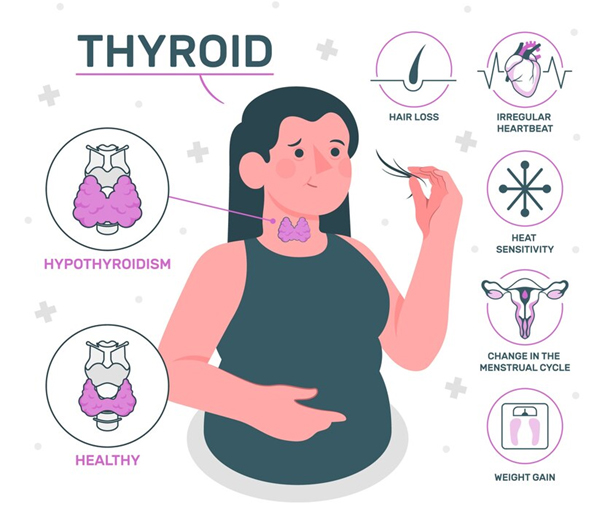
Understanding Hypothyroidism and Goiter
Hypothyroidism is a common condition where the thyroid gland fails to produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to a slower metabolic rate. Goiter, on the other hand, refers to the enlargement of the thyroid gland. Both conditions often go hand in hand, as goitre can be a manifestation of hypothyroidism.
Cause of Hypothyroidism
Several things can cause the thyroid gland to enlarge. Some of the most common are :
- Iodine deficiency
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, and is found primarily in seawater and in the soil in coastal areas. In the developing world, people who live inland or at high elevations are often iodine deficient and can develop goitres when the thyroid enlarges in an effort to obtain more iodine. Iodine deficiency may be made worse by a diet high in hormone-inhibiting foods, such as cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower. In countries where iodine is routinely added to table salt and other foods, a lack of dietary iodine isn't usually the cause of goitres.
- Graves' disease
A goitre can sometimes occur when your thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism). In someone who has Graves' disease, antibodies produced by the immune system mistakenly attack the thyroid gland, causing it to produce excess thyroxine. This overstimulation causes the thyroid to swell.
- Hashimoto's disease
A goitre can also result from an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Like Graves' disease, Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder. But instead of causing your thyroid to produce too much hormone, Hashimoto's damages your thyroid so that it produces too little.
- Multinodular goitre
Sensing a low hormone level, the pituitary gland produces more TSH to stimulate the thyroid, which then causes the gland to enlarge.
- Solitary thyroid nodules
In this case, a single nodule develops in one part of your thyroid gland. Most nodules are noncancerous (benign) and don't lead to cancer.
- Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is far less common than benign thyroid nodules. A biopsy of a thyroid nodule is very accurate in determining whether it's cancerous.
- Pregnancy
A hormone produced during pregnancy, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), may cause your thyroid gland to enlarge slightly.
- Inflammation
Thyroiditis is an inflammatory condition that can cause pain and swelling in the thyroid. It may also cause the body to produce too much or too little thyroxine.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
The primary symptom of a goitre is noticeable swelling in your neck.If you have nodules on your thyroid, they may range in size from very small to very large.
The presence of nodules may increase the appearance of swelling.
- Other Common symptoms include the following
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Coughing
- Hoarseness
- Dizziness when raise arm above head
- A swelling at the base of neck that may be particularly obvious when shave or put on makeup
- A tight feeling in throat
- Other, less common symptoms include :
- Difficulty breathing (shortness of breath)
- Coughing
- Wheezing (due to squeezing of the windpipe)
- Difficulty swallowing (due to squeezing of the oesophagus, or “food tube”)
Some people who have a goitre may also have hyperthyroidism, or overactive thyroid.
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include :
- An increased resting pulse rate
- Rapid heartbeat
- Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting
- Sweating without exercise or increased room temperature
- Shaking
- Agitation
Some people with goitre may also have hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid.
- Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include :
- Fatigue (feeling tired)
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Weight gain
- Menstrual irregularities
Types of Goiter
Goitres have many causes. As a result, there are different types. These include:
- Colloid goitre (endemic)
A colloid goitre develops from the lack of iodine, a mineral essential to the production of thyroid hormones. People who get this type of goitre usually live in areas where iodine is scarce.
- Nontoxic goitre (sporadic)
The cause of a nontoxic goitre is usually unknown, though it may be caused by medications like lithium. Lithium is used to treat mood disorders such as bipolar disorder. Non Toxic goitres don’t affect the production of thyroid hormone, and thyroid function is healthy. They’re also benign.
- Toxic nodular or multinodular goitre
This type of goitre forms one or more small nodules as it enlarges. The nodules produce their own thyroid hormone, causing hyperthyroidism. It generally forms as an extension of a simple goitre.
Risk factors of Hyperthyroidism
Goitres can affect anyone. They may be present at birth and occur at any time throughout life.
Some common risk factors for goitres include :
- A lack of dietary iodine
People living in areas where iodine is in short supply and who don't have access to iodine supplements are at high risk of goitres.
- Being female
Because women are more prone to thyroid disorders, they're also more likely to develop goitres.
- Your age
Goitres are more common after age 40.
- Medical history
A personal or family history of autoimmune disease increases your risk.
- Pregnancy and menopause
For reasons that aren't entirely clear, thyroid problems are more likely to occur during pregnancy and menopause.
- Certain medications
Some medical treatments, including the heart drug amiodarone (Pacerone, others) and the psychiatric drug lithium (Lithobid, others), increase your risk.
- Radiation exposure
Your risk increases if you've had radiation treatments to your neck or chest area or you've been exposed to radiation in a nuclear facility, test or accident.
Complication of Hyperthyroidism
Small goitres that don't cause physical or cosmetic problems aren't a concern. But large goitres can make it hard to breathe or swallow and can cause a cough and hoarseness. Goitres that result from other conditions, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, may be associated with a number of symptoms, ranging from fatigue and weight gain to unintended weight loss, irritability and trouble sleeping.
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
Doctors may discover an enlarged thyroid gland simply by feeling your neck and having you swallow during a routine physical exam. In some cases, doctors may also be able to feel the presence of nodules.
Diagnosing a goitre may also involve :
- A hormone test
Blood tests can determine the amount of hormones produced by your thyroid and pituitary glands. If your thyroid is underactive, the level of thyroid hormone will be low. At the same time, the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) will be elevated because your pituitary gland tries to stimulate your thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormone. A goitre associated with an overactive thyroid usually involves a high level of thyroid hormone in the blood and a lower than normal TSH level.
- An antibody test
Some causes of a goitre involve production of abnormal antibodies. A blood test may confirm the presence of these antibodies.
- Ultrasonography
A wand-like device (transducer) is held over your neck. Sound waves bounce through your neck and back, forming images on a computer screen. The images reveal the size of your thyroid gland and whether the gland contains nodules that your doctor may not have been able to feel.
- A thyroid scan
During a thyroid scan, a radioactive isotope is injected into the vein on the inside of your elbow. You lie on a table with your head stretched backward while a special camera produces an image of your thyroid on a computer screen. The time needed for the procedure may vary, depending on how long it takes the isotope to reach your thyroid gland. Thyroid scans provide information about the nature and size of your thyroid, but they're more invasive, time-consuming and expensive than ultrasound tests.
- A biopsy
During a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, ultrasound is used to guide a needle into your thyroid to obtain a tissue or fluid sample for testing.
Homeopathy and Hypo Goiter
Homeopathy, a holistic system of medicine, offers a gentle and personalised approach to addressing hypo goitre. Homoeopathic remedies aim to stimulate the body's inherent healing ability, promoting balance and overall well-being. The selection of a specific homoeopathic remedy is based on an individual's unique symptoms, constitution, and underlying causes of the condition.
Key Benefits of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Individualised Approach: Homoeopathy recognizes that each person is unique. A homoeopath will assess your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle to prescribe a personalised treatment plan tailored to your needs.
- Gentle and Natural: Homoeopathic remedies are derived from natural substances and are known for their minimal side effects. They work in harmony with the body, promoting self-healing and overall well-being.
- Holistic Well-being: Homoeopathy takes into account not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and mental aspects of an individual. It aims to restore balance at all levels, providing comprehensive care.
- Long-Term Results: Homeopathy aims to address the underlying causes of the condition rather than merely suppressing symptoms. By stimulating the body's healing mechanisms, it can potentially lead to long-lasting improvement.
Homoeopathic medication for Goitre
- Iodum
For Hyperactive Thyroid and Accelerated Metabolic Functions
- Iodum is one of the top listed medicines for goitre. It is used when the thyroid gland is enlarged, hyperactive and the metabolic functions of the body are accelerated.
- The thyroid gland may also be indurated and hard along with its enlargement. Due to the increased metabolic rate, the person in need of Iodum for goitre goes on losing weight even after eating a lot.
- The appetite is increased, but the person does not gain weight. Another symptom to look out for prescription of Iodum as one of the best medicines for goitre is that the person feels very hot and constantly in need of cool air.
- Mentally, such persons are nervous, restless, hurried and impulsive, with extreme mental excitement. Iodum is also considered the most effective among medicines for goitre where tachycardia is present with a rapid, accelerated pulse rate.
- Palpitations may arise from the least exertion. Iodum also helps treat women with goitre where chronic amenorrhoea is present.
- Another set of symptoms for prescribing Iodum in goitre includes chronic diarrhoea with weakness, bulging/protruding eyes, deep and hoarse voice.
- Calcarea Carb
For Enlarged Thyroid and Slow Metabolic Functions
- Calcarea Carb is helpful in cases of goitre where the thyroid gland is enlarged but underactive, with a slowed down metabolism.
- For using Calcarea Carb in goitre, the hallmark symptom is sluggishness of all body functions. Tiredness, slowness on the mental and physical plane are marked.
- There are other varying symptoms that guide use of Calcarea Carb as one of the top medicines for goitre. The first among these is obesity.
- A person who needs prescribing Calcarea Carb is fat, obese and goes on gaining weight even with a normal appetite. The second important symptom is chilliness with marked intolerance to cold.
- Persons who need Calcarea Carb usually suffer chronic constipation as well.
- The constitutional symptoms that are important to look out for include profuse sweating over the scalp, craving for eggs and indigestible things such as chalk, lime and pencils, and aversion to fatty food.
- Spongia
- Spongia is highly recommended among medicines for goitre where the thyroid gland is much swollen and enlarged.
- The chin, too, swells along with the thyroid gland. Applying pressure on the thyroid gland causes pain in such cases.
- Spongia is also one of the most helpful medicines for goitre with suffocative episodes appearing from time to time. Dry, tickling cough in goitre patients can also be managed well with medicine Spongia.
- Natrum Mur - Constitutional Remedy for Goiter
- Natrum Mur is rated among the most effective constitutional medicines for goitre. If selected as per unique constitutional symptoms, Natrum Mur holds great promise of recovery for goitre patients.
- Natrum Mur works best in reserved, introverted personalities that are prone to depression, weeping spells and feelings of loneliness. Irritability, restlessness and nervousness are high among such subjects. Physically, they appear emaciated, with the neck showing maximum thinning. Excessive exhaustion and weakness accompanies the condition.
- The eyes also show protrusion. Natrum Mur is quite successful in dealing with tachycardia and palpitations due to goitre as well. Palpitations are violent, shaking the whole body and they get worse with emotions or exertion.
- In women with goitre, Natrum Mur works as one of the most reliable medicines for goitre and can help regulate irregular periods. It must be noted, however, that most people prescribed Natrum Mur show marked intolerance to heat and have trouble tolerating the sun. Extra craving for salt may also be felt by persons who need Natrum Mur for goitre treatment.
- Fucus Vesiculosus and Lycopus
- Fucus Vesiculosus is a highly effective remedy for goitre.
- It yields excellent results in obese persons suffering from enlarged thyroid gland (goitre).
- Fucus Vesiculosus is also one of the most effective medicines for goitres of non-toxic nature.
- Lycopus is recommended for toxic goitres.
- Lycopus can be used in goitre patients who show protruding eyeballs with heart involvement.
- Breathlessness and inability to exert in any kind of work also hint at Lycopus as the most effective medicines for goitre with these symptoms.
- Bromium
- Most marked effects are seen in the respiratory symptoms, especially in the larynx and trachea.
- Enlarged parotid and goitre.
- Sense of suffocation.
- Complaints from being overheated.
- Conium Mac
- Hard nodular swelling of glands. Conium has been used extensively for malignant affections of glands, because it takes hold of glands from the beginning and infiltrates, and they gradually grow to a stony hardness; like scirrhous.
- Weakness and trembling of the body and mind, palpitations.
- Heavy, weary, paralysed, trembling hands
- Muscular weakness, specially of the lower extremities.
- Depressed, timid, averse to society, and afraid of being alone.
- No inclination for business or study; takes no interest in anything. Memory weak; unable to sustain any mental effort.
- Pilocarpus Microphyllus
- Acts upon thyroid gland.
- Exophthalmic goitre, with increased heart's rate and sweating
- Ferrum Iodatum
- Glandular enlargements, and tumours call for this remedy
- Exophthalmic goitre following suppression of menses
- Duboisia
- Acts on thyroid gland and acts as a palliative in case of exophthalmic goitre.
- Thyroidinum
- Thyroid produces anaemia, emaciation, muscular weakness, sweating, headache, nervous tremor of face and limbs, tingling sensations, paralysis. Heart rate increased, exophthalmos and dilation of pupils.
- Thyroid weakness causes craving for a large amount of sweets.
- Eyeballs prominent. Face flushed. Tongue thickly coated. Fullness and heat. Bad taste in mouth.
- Irritable, worse least opposition
- Natrum carb
- All the Natrums stimulate cellular activity and increase oxidation and metabolism. Great debility caused by summer heat; chronic effects of sunstroke; exhaustion; anaemic; milky, watery skin; very weak ankles, are all peculiar Natrum carbonicum conditions.
- Mental weakness and depression; worries; very sensitive to noise; colds, change of weather. Anxious and restless during thunderstorms; worse from music (Ambra). Marked gayety. Sensitive to the presence of certain individuals.
- Skin inclination to perspire easily, or dry, rough, cracked skin. Eruption on finger-tips, knuckles and toes. Vesicular eruption in patches and circles.
- Great weakness of limbs, especially in the morning.
Patient Review
Consulting a Homeopath
If you're seeking homoeopathic treatment for hypo goitre, consulting a qualified and experienced homoeopath is crucial. A professional Sanjivani homoeopath will conduct a detailed assessment of your symptoms, medical history, and individual characteristics to determine an appropriate treatment plan.
Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic USP
- No homoeopathy Dietary Restrictions:
Allows patients to enjoy foods like onion, garlic, and coffee, ensuring a stress-free treatment journey.
- 24/7 Online Consultations:
Enables convenient access to doctors with detailed counseling, history management, and follow-ups.
- Highly Skilled Team:
Experienced BHMS and MD doctors, supported by multilingual and professional staff.
- Patient-Centric Care:
Simplifies treatment with modern, adaptable solutions and clear communication.
Click Here for Detailed "Sanjivani USP"
FAQ's
- What is homoeopathy ?
Homoeopathy is a holistic science which belives in the law of Similia Similibus Curenter i.e Like Cures Like .It was discovered by Dr Samuel Christian Hahnemannn in 1796.
- Is there any side effects of homoeopathy?
As homoeopathic medicines are made from natural substances this medicines have no side effects and are completely safe to consume
- Is there any diet restriction to take homoeopathic medicines?
There are no diet restrictions for homoeopathic medicines. One should only avoid eating or drinking any liquid other than water at least 30 minutes before and after taking homoeopathic medicines.
Click Here for "Frequently Asked Questions."
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism and goitre can significantly impact one's quality of life, but with the holistic approach of homoeopathy, there is hope for relief and restoration. The Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic is dedicated to providing personalised and effective treatment options for patients with hypo goitre. Our team of skilled homoeopaths is committed to addressing the root causes of your condition and supporting your overall well-being.
Remember, homoeopathy is a safe and gentle healing system that can complement conventional treatments. If you're experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism or have concerns about goitre, reach out to our clinic today. Let us guide you on the path to optimal thyroid health and vibrant life!
Disclaimer : The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any treatment for Hypothyroidism and Goitre or any other medical condition.


