Introduction
The term sexually transmitted disease (STD) is used to refer to a condition passed from one person to another through sexual contact. They can contract an STD by having unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the STD.An STD may also be called a sexually transmitted infection (STI)

Understanding STD
STDs used to be called venereal diseases or VD. They are among the most common contagious diseases.That doesn’t mean sex is the only way STDs are transmitted. Depending on the specific STD, infections may also be transmitted through sharing needles and breastfeeding. They can affect people of all ages, genders, sexual orientations, and socioeconomic backgrounds. Understanding the basics of STDs is essential for individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual health and well-being.
Types of STD
- HIV
- Chlamydia
- Genital herpes
- Genital warts
- Gonorrhea
- Some forms of hepatitis
- Syphilis
- Trichomoniasis
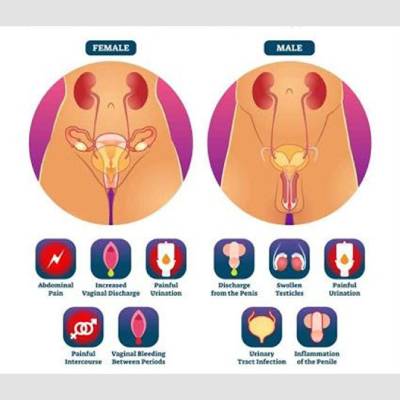
Symptoms of STDs in Mens
It’s possible to contract an STD without developing symptoms. But some STDs cause obvious symptoms. In men, common symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort during sex or urination
- Sores, bumps, or rashes on or around the penis, testicles, anus, buttocks, thighs, or mouth
- Unusual discharge or bleeding from the penis
- Painful or swollen testicles
- Specific symptoms can vary, depending on the STD.

Symptoms of STDs in Womens
In many cases, STDs don’t cause noticeable symptoms. When they do, common STD symptoms in women include:
- Pain or discomfort during sex or urination
- Sores, bumps, or rashes on or around the vagina, anus, buttocks, thighs, or mouth
- Unusual discharge or bleeding from the vagina
- Itchiness in or around the vagina
- The specific symptoms can vary from one STD to another.
Types of STD
Many different types of infections can be transmitted sexually. The most common STDs are described below.
1. Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is another common bacterial STD, also known as “the clap.” Many people with gonorrhea develop no symptoms. But when present, symptoms may include:- A white, yellow, beige, or green-colored discharge from the penis or vagina
- Pain or discomfort during sex or urination
- More frequent urination than usual
- Itching around the genitals
- Sore throat
- Thick, cloudy, or bloody discharge from the penis or vagina
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Heavy menstrual bleeding or bleeding between periods in females
- Painful, swollen testicles in males
- Painful bowel movements
- Anal itching
If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to serious health problems. It’s possible for a mother to pass gonorrhea onto a newborn during childbirth, which can cause serious health issues in the baby.
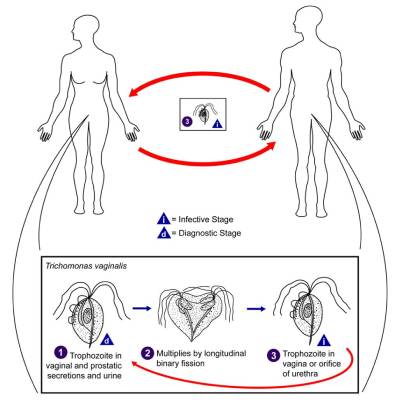
2. Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, also known as “trich,” is caused by a tiny protozoan organism that can be passed from one person to another through genital contact. When symptoms do develop, they may include:- Discharge from the vagina or penis
- Burning or itching around the vagina or penis
- Pain or discomfort during urination or sex
- Frequent urination
- In women, trich-related discharge often has an unpleasant or “fishy” smell
- Clear, white, greenish, or yellowish vaginal discharge
- Discharge from the penis
- Strong vaginal odor
- Vaginal itching or irritation
- Itching or irritation inside the penis
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Painful urination
If left untreated, trichomoniasis can lead to:
- Infections of the urethra
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Infertility
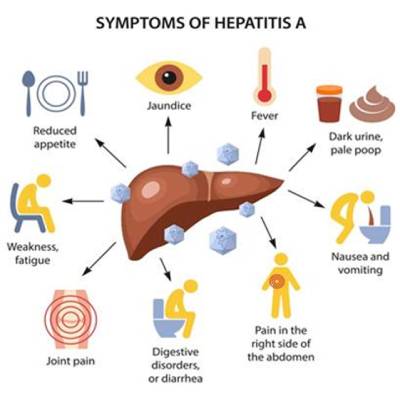
3. Hepatitis
Hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C are all contagious viral infections that affect your liver. Hepatitis B and C are the most serious of the three, but each can cause your liver to become inflamed. Some people never develop signs or symptoms. But for those who do, signs and symptoms may occur several weeks after exposure and may include:- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, especially in the area of your liver on your right side beneath your lower ribs
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Dark urine
- Muscle or joint pain
- Itching
- Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice)
4. Chlamydia
A certain type of bacteria causes chlamydia. Many people with chlamydia have no noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do develop, they often include:- Pain or discomfort during sex or urination
- Green or yellow discharge from the penis or vagina
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Painful urination
- Lower abdominal pain
- Vaginal discharge in women
- Discharge from the penis in men
- Pain during sexual intercourse in women
- Bleeding between periods in women
- Testicular pain in men
If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to:
- Infections of the urethra, prostate gland, or testicles
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Infertility
If a pregnant woman has untreated chlamydia, she can pass it to her baby during birth. The baby may develop:
- Pneumonia
- Eye infections
- Blindness
5. HPV (human papillomavirus) and genital warts
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a virus that can be passed from one person to another through intimate skin-to-skin or sexual contact. There are many different strains of the virus, some of which are more dangerous than others. The most common symptom of HPV is warts on the genitals, mouth, or throat. The signs and symptoms of genital warts include:- Small, flesh-colored or grey swellings in your genital area
- Several warts close together that take on a cauliflower shape
- Itching or discomfort in your genital area
- Bleeding with intercourse
Some strains of HPV infection can lead to cancer, including:
- Oral cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Vulvar cancer
- Penile cancer
- Rectal cancer
While most cases of HPV don’t become cancerous, some strains of the virus are more likely to cause cancer than others.
6. Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that often goes unnoticed in its early stages. The first symptom to appear is a small round sore, known as a chancre, which can develop on your genitals, anus, or mouth. It’s painless but very infectious. Syphilis affects your genitals, skin, and mucous membranes, but it can also involve other parts of your body, including your brain and heart. The signs and symptoms of syphilis may occur in three stages — primary, secondary, and tertiary. Some people also experience latent syphilis, in which blood tests are positive for the bacteria but no symptoms are present.- At first, only a small, painless sore (chancre) may be present at the site of infection. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include:
- Rash marked by red or reddish-brown, penny-sized sores over any area of your body, including your palms and soles
- Fever
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Fatigue and a vague feeling of discomfort
- Soreness and aching
Without treatment, syphilis bacteria may spread, leading to serious internal organ damage and death years after the original infection.
Signs and Symptoms: Syphilis has three stages, and the symptoms vary by stage.
- Primary Syphilis: A small, firm, and round sore (chancre) forms at the site from where bacteria entered the body (penis, vagina, anus, or mouth). The chancre usually appears around three weeks after exposure and typically heals and disappears within 3 to 6 weeks.
- Secondary Syphilis: This stage arises after the healing of the chancre. A rash appears on the trunk and covers the full body. The rash may be red or reddish-brown. Other symptoms may include sore throat, muscle aches, fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, and patchy hair loss. These symptoms may disappear in a few weeks or return many times. If not treated, it can progress to a latent stage with no symptoms.
- Tertiary Syphilis: This can occur many years (even 10 to 30 years) after the onset of the infection, after the latent asymptomatic stage. Symptoms can include:
- Rash
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Headaches
- Joint pain
- Weight loss
- Hair loss
Some signs and symptoms of late-stage syphilis include:
- Lack of coordination
- Numbness
- Paralysis
- Blindness
- Dementia
If left untreated, late-stage syphilis can lead to:
- Loss of vision
- Loss of hearing
- Loss of memory
- Mental illness
- Infections of the brain or spinal cord
- Heart disease
- Death
7. Neurosyphilis
At any stage, syphilis can affect the nervous system. Neurosyphilis may cause no signs or symptoms, or it can cause:- Headache
- Behaviour changes
- Movement problems
8. HIV
HIV can damage the immune system and raise the risk of contracting other viruses or bacteria and certain cancers. If left untreated, it can lead to stage 3 HIV, known as AIDS. In the early or acute stages, it’s easy to mistake the symptoms of HIV with those of the flu. Early HIV signs and symptoms usually disappear within a week to a month and are often mistaken for those of another viral infection. During this period, you're highly infectious. More persistent or severe symptoms of HIV infection may not appear for 10 years or more after the initial infection. The early symptoms can include:- Fever
- Chills
- Aches and pains
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Nausea
- Rashes
- Swollen lymph nodes — often one of the first signs of HIV infection
- Diarrhoea
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Cough and shortness of breath
Late-stage HIV infection signs and symptoms include:
- Persistent, unexplained fatigue
- Soaking night sweats
- Shaking chills or fever higher than 100.4 F (38 C) for several weeks
- Swelling of lymph nodes for more than three months
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Persistent headaches
- Unusual, opportunistic infections
These initial symptoms typically clear within a month or so. From that point onward, a person can carry HIV without developing serious or persistent symptoms for many years. Other people may develop nonspecific symptoms, such as:
- Recurrent fatigue
- Fevers
- Headaches
- Stomach issues
- Infections of the urethra, prostate gland, or testicles in males
- Pelvic inflammatory disease in females
- Infertility
9. Pubic lice (crabs)
“Crabs” is another name for pubic lice. They’re tiny insects that can take up residence on your pubic hair. Like head lice and body lice, they feed on human blood. Common symptoms of pubic lice include:- Itching around the genitals or anus
- Small pink or red bumps around the genitals or anus
- Low-grade fever
- Lack of energy
- Irritability
You might also be able to see the lice or their tiny white eggs around the roots of pubic hair. If left untreated, pubic lice can spread to other people through skin-to-skin contact or shared clothing, bedding, or towels. Scratched bites can also become infected.
10. Herpes
Herpes is the shortened name for the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two main strains of the virus, HSV-1 and HSV-2. Both can be transmitted sexually. It’s a very common STD.- HSV-1: Primarily causes oral herpes, responsible for cold sores. However, HSV-1 can also be passed from one person’s mouth to another person’s genitals during oral sex, causing genital herpes.
- HSV-2: Primarily causes genital herpes.
The most common symptom of herpes is blistery sores. In genital herpes, these sores develop on or around the genitals; in oral herpes, they develop on or around the mouth. Herpes sores generally crust over and heal within a few weeks. The first outbreak is usually the most painful, and outbreaks typically become less painful and frequent over time.
If a pregnant woman has herpes, she can potentially pass it to her fetus in the womb or to her newborn infant during childbirth. This so-called congenital herpes can be very dangerous to newborns. That’s why it’s beneficial for pregnant women to become aware of their HSV status.
11. Genital herpes
Genital herpes is a highly contagious STI caused by a type of herpes simplex virus (HSV) that enters your body through small breaks in your skin or mucous membranes. Most people with HSV never know they have it, because they have no signs or symptoms, or the signs and symptoms are so mild they go unnoticed. When signs and symptoms are noticeable, the first episode is generally the worst. Some people never have a second episode, while others can have recurrent episodes for decades.When present, genital herpes signs and symptoms may include:
- Small red bumps, blisters (vesicles), or open sores (ulcers) in the genital and anal areas and nearby regions.
- Pain or itching around the genital area, buttocks, and inner thighs.
- Ulcers can make urination painful, and there may also be pain and tenderness in the genital area until the infection clears.
During an initial episode, you may have flu-like signs and symptoms such as:
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
In some cases, the infection can be active and contagious even when sores aren't present.
12. Vaginitis
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina that can result in discharge, itching, and pain. The cause is usually a change in the normal balance of vaginal bacteria or an infection. Reduced estrogen levels after menopause and some skin disorders can also cause vaginitis.
The most common types of vaginitis are:
- Bacterial vaginosis: results from a change of the normal bacteria found in your vagina to overgrowth of other organisms.
- Yeast infections: usually caused by a naturally occurring fungus called Candida albicans.
- Trichomoniasis: caused by a parasite and is commonly transmitted by sexual intercourse.
Symptoms
Vaginitis signs and symptoms can include:
- Change in colour, odour, or amount of discharge from your vagina.
- Vaginal itching or irritation.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Painful urination.
- Light vaginal bleeding or spotting.
Characteristics of Discharge
Have vaginal discharge? The characteristics of the discharge might indicate the type of vaginitis. Examples include:
- Bacterial vaginosis: might develop a greyish-white, foul-smelling discharge, often described as a fishy odour, which may be more noticeable after sexual intercourse.
- Yeast infection: main symptom is itching, but there might be a white, thick discharge that resembles cottage cheese.
- Trichomoniasis: can cause a greenish-yellow, sometimes frothy discharge.
Diagnosis
To diagnose vaginitis, your doctor may:
- Review your medical history, including your history of vaginal or sexually transmitted infections.
- Perform a pelvic exam, using an instrument (speculum) to look inside your vagina for inflammation and abnormal discharge.
- Collect a sample for lab testing to confirm what kind of vaginitis you have.
- Perform pH testing using a pH test stick or paper. An elevated pH can indicate either bacterial vaginosis or trichomoniasis, but pH testing alone is not a reliable diagnostic test.
Causes of STIs and STDs
There are three major causes of STDs/STIs:
- Bacteria: including chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
- Viruses: including HIV/AIDS, herpes simplex virus, human papillomavirus, hepatitis B virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Zika.
- Parasites: such as Trichomonas vaginalis, or insects such as crab lice or scabies mites.
Any STI can be spread through sexual activity, including sexual intercourse. Some STIs can also be spread through oral sex and other sexual activities. Ejaculation does not have to occur for an STI to pass from person to person.
In addition, sharing contaminated needles, such as those used to inject drugs, or using contaminated body piercing or tattooing equipment can transmit some infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. A few infections can be sexually transmitted but are also spread through nonsexual, close contact. Some of these infections, like CMV, are not considered STIs even though they can be transmitted through sexual contact.
Diagnosis
Tests
If your sexual history and current signs and symptoms suggest that you have a sexually transmitted disease (STD) or a sexually transmitted infection (STI), laboratory tests can identify the cause and detect coinfections you might also have:
- Blood tests: Can confirm the diagnosis of HIV or later stages of syphilis.
- Urine samples: Some STIs can be confirmed with a urine sample.
- Fluid samples: If you have open genital sores, fluid and samples from the sores may be tested to diagnose the type of infection.
Screening
Testing for a disease in someone who doesn't have symptoms is called screening. Most of the time, STI screening is not a routine part of health care, but there are exceptions:
- Everyone: A blood or saliva test for HIV is recommended for everyone ages 13 to 64. People at high risk should have an HIV test every year.
- Pregnant women: All pregnant women are generally screened for HIV, hepatitis B, chlamydia, and syphilis at their first prenatal visit. Gonorrhea and hepatitis C screening tests are recommended at least once during pregnancy for women at high risk.
- Women aged 21 and older: The Pap test screens for cervical abnormalities, including inflammation and precancerous changes. It is recommended every three years starting at age 21, and every five years after age 30 with HPV DNA testing.
- Women under age 25 who are sexually active: All sexually active women under age 25 should be tested for chlamydia infection using a urine or vaginal fluid sample.
- Men who have sex with men: Regular STI screening is recommended due to higher risk. Tests for HIV, syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea are particularly important.
- People with HIV: Immediate testing for syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and herpes is recommended after being diagnosed with HIV. Screening for hepatitis C is also advised.
- Women with HIV: They should have a Pap test within a year of being diagnosed with HIV, followed by another six months later.
- People who have a new partner: Both partners should be tested for STIs before engaging in vaginal or anal intercourse. Routine testing for genital herpes isn't recommended unless symptoms are present.
Homoeopathy and STD
Homoeopathy offers natural and individualised remedies for managing STD . By considering the patient's unique symptoms, triggers, and overall health, homoeopathic practitioners prescribe remedies that aim to restore balance to the body and alleviate symptoms. Remedies are chosen based on individual symptoms, triggers, and constitutional factors, offering personalised treatment options for patients.
Homeopathic Medicines for Chlamydia
- Sepia
Manages vaginal discharge (yellow, greenish, clear, or milky white). Symptoms may worsen after urination, with acrid discharge causing burning and itching. Frequent urination and pelvic pain are also common. - Kreosote
Treats offensive vaginal discharge with a putrid odor (yellow or white). Symptoms include acrid discharge causing itching, soreness, and burning in the genitals, worsening with movement. - Natrum Mur
Alleviates painful intercourse in females. Symptoms include burning, smarting during coition, and either dry or profuse vaginal discharge (transparent and watery). - Argentum Nitricum
Manages bleeding after intercourse. Symptoms include painful coition and profuse yellow discharge, sometimes blood-stained. - Petroselinum
For males with milky urethral discharge. Symptoms include itching and crawling sensations in the urethra, with a frequent urge to urinate. - Cannabis Sativa
Treats yellow, watery urethral discharge in males. Accompanied by burning during urination, straining, and scanty urine. - Pulsatilla
For males with yellowish-green urethral discharge. Symptoms include thick discharge, pain, swelling, and burning in the testicles. - Cantharis
Manages burning and painful urination. Symptoms include severe cutting pain during urination, frequent urination, and sometimes jelly-like particles in urine. - Merc Sol
Treats frequent urination, urgency, and burning. Symptoms include yellow or green urethral discharge and increased urgency to urinate. - Rhododendron
Alleviates testicular pain and swelling. Symptoms include varying pain types (pressing, tearing) that worsen with sitting.
Homeopathic Medicines for Syphilis
- Medorrhinum
Top treatment for gonorrhea. Symptoms include burning urethral pain, offensive urine smell, and thick, acrid vaginal discharge in females. - Cannabis Sativa
Treats watery mucus or purulent discharge in males. Symptoms include burning pain while urinating and constant desire to urinate. - Nitric Acid
Manages yellow-green urethral discharge in males. Symptoms include intense pain while urinating and possible blood-stained discharge. - Rhododendron
For gonorrhea with swollen, painful testicles. Symptoms include hard testicles and pain that worsens with sitting. - Cantharis
Treats painful and burning urination. Symptoms include severe urethral pain, frequent urination, and scanty urine. - Merc Sol
For increased frequency and urgency to urinate. Symptoms include thick yellow or green urethral discharge. - Pulsatilla
For females with white, acrid vaginal discharge. Symptoms include marked burning and discomfort. - Sepia
Effective for females with greenish vaginal discharges. Symptoms include profuse discharge after urination and painful coition.
Homeopathic Medicines for Vaginitis
- Pulsatilla – For vaginitis with thick vaginal discharge
Helpful when vaginal discharges are thick like cream, white (like milk), and worsen when lying down. May include burning in the vagina and backache. - Kreosote – For itching in vagina
Natural remedy for intense vaginal itching, soreness, and burning after scratching. Discharges may be white or yellow with a putrid smell, worsening with movement. - Alumina – For vaginitis with burning in vagina
Natural cure for burning due to discharges that worsen during the day. Discharges may be transparent or light yellow, highly acrid, and excoriating. - Merc Sol
Treats vaginitis with greenish discharges, often blood-stained, corrosive, and itchy. Symptoms include burning during urination and swelling of the genitals. - Hydrastis
For vaginitis with yellow discharge that is profuse, thick, and may be offensive. Itching occurs due to the discharges. - Graphites
Manages profuse, gushing white or yellowish-white discharges that are acrid and excoriate the skin, causing biting pain and weakness in the back. - Nitric Acid
Natural medicine for offensive vaginal discharges that may vary in color (green, brown, clear). Causes burning in the vulva and vagina, and stitching pain. - Natrum Phos
Effective for sour-smelling vaginal discharges that may be creamy or watery and often honey-colored. - Medorrhinum
Natural remedy for vaginitis with a fishy odor and thick, acrid discharges, often associated with excessive itching.
Homeopathic Medicines for Herpes
- Arsenicum Album
Ulceration in the mouth and tongue with burning sensations. Dry, scaly skin eruptions worsen with cold. Swelling and discoloration of the penis in genital herpes. Symptoms include extreme restlessness and anxiety about health. - Graphites
Blisters on the tongue and ulcers on the lips. Thin, profuse vaginal discharge and herpetic eruptions on the penis. - Hepar Sulphuris
Painful eruptions and ulcers on the mouth. Sensitive abscesses on the genitals with a cheesy odor. Symptoms worsen during menses. - Mercurius Solubilis
Pustular yellow scabs and ulcers on the lips. Profuse salivation and thirst. Greenish, corroding vaginal discharge that increases at night. - Natrum Muriaticum
Eruptions on the tongue with burning sensations and pearl-like vesicles on the lips. Thick, transparent vaginal discharge with itching. - Petroleum
Painful scabby pimples on the lips and around the mouth. Itchy eruptions around the anal region and thighs. Profuse white discharge from the vagina. - Rhus Tox
Fluid-filled lesions around the mouth. Ulceration and inflammation of the genitals. - Sepia
Yellow herpetic eruptions around the mouth, painful ulcers on the lips, and burning sensations in the cervix with yellow, green discharge.
Benefits of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Individualised Care: Homoeopathy recognizes that each person's experience with migraines and headaches is unique. A homoeopath will assess the symptoms, triggers, medical history, and individual characteristics to prescribe a personalised treatment plan tailored to the individual's needs.
- Gentle and Natural: Homoeopathic remedies are derived from natural substances and are known for their safety and minimal side effects. They work in harmony with the body, promoting self-healing and overall well-being.
- Holistic Approach: Homoeopathy considers not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and mental aspects of an individual. It aims to restore balance at all levels, providing comprehensive care.
- Long-Term Results: By addressing the underlying causes of migraines and headaches, homoeopathy strives to achieve long-term relief, reduce the frequency and intensity of episodes, and improve overall well-being.
Consulting a Homeopath
Consulting a qualified Sanjivani homoeopath is essential for accurately diagnosing and effectively treating STD . During the consultation, the Sanjivani homoeopath evaluates the patient's symptoms, medical history, and potential triggers, often using diagnostic tools like physical exams, blood tests. By understanding the root cause of the condition and considering the patient's overall health and lifestyle, Sanjivani homoeopath prescribes appropriate homoeopathic remedies tailored to address the individual's specific needs.
Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic USP
- No homoeopathy Dietary Restrictions:
Allows patients to enjoy foods like onion, garlic, and coffee, ensuring a stress-free treatment journey.
- 24/7 Online Consultations:
Enables convenient access to doctors with detailed counseling, history management, and follow-ups.
- Highly Skilled Team:
Experienced BHMS and MD doctors, supported by multilingual and professional staff.
- Patient-Centric Care:
Simplifies treatment with modern, adaptable solutions and clear communication.
Click Here for Detailed "Sanjivani USP"
FAQ's
- What is homoeopathy ?
Homoeopathy is a holistic science which belives in the law of Similia Similibus Curenter i.e Like Cures Like .It was discovered by Dr Samuel Christian Hahnemannn in 1796.
- Is there any side effects of homoeopathy?
As homoeopathic medicines are made from natural substances this medicines have no side effects and are completely safe to consume
- Is there any diet restriction to take homoeopathic medicines?
There are no diet restrictions for homoeopathic medicines. One should only avoid eating or drinking any liquid other than water at least 30 minutes before and after taking homoeopathic medicines.
Click Here for "Frequently Asked Questions."
Conclusion
STD’s, can significantly impact an individual's well-being. While conventional treatments focus on symptom management, Sanjivani homoeopathy offers a holistic approach to address the underlying causes and alleviate symptoms effectively. By consulting a qualified Sanjivani homoeopath and receiving personalised treatment, individuals with urticaria can experience relief and improve their quality of life naturally and safely.
Disclaimer :The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any treatment for STD or any other medical condition.


