Introduction
Welcome to the Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic blog! Today, we address the topic of Eczema, a condition where patches of skin become inflamed, itchy, cracked, and rough. Some types can also cause blisters. Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common and chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide
It is characterised by itchy, red, and inflamed skin patches that can be both physically and emotionally distressing. Eczema can manifest at any age, but it often begins in early childhood and can persist into adulthood. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, conventional treatments, and the promising role of homoeopathy in providing natural support, relieving symptoms, and improving skin health for individuals with eczema. Join us on this journey to discover a holistic approach to managing eczema at Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic.
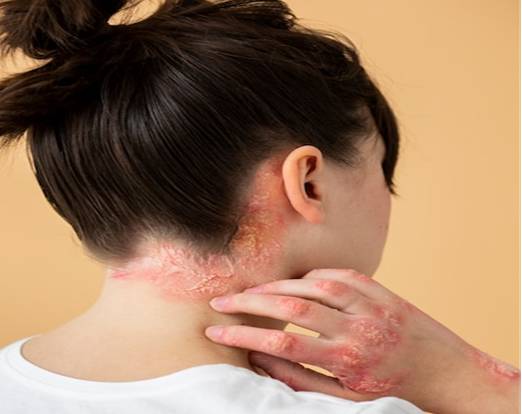
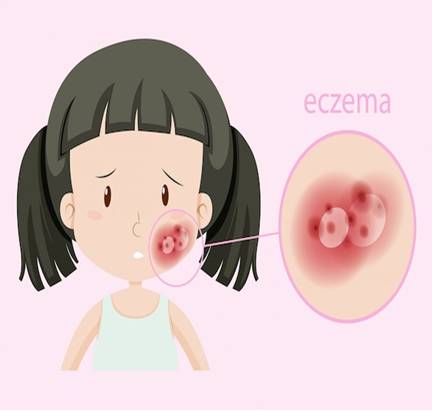
Understanding Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that often begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood. It is characterised by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, which can lead to redness, swelling, and the development of rashes. Eczema can be triggered by various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental allergens, stress, and immune system dysfunction.
Types of Eczema
1. Atopic Dermatitis :
Atopic dermatitis, the most prevalent form of eczema, has a genetic component and typically manifests in childhood. Although it shares a connection with inhalant allergies, atopic dermatitis itself is not solely an allergic reaction. Commonly, the condition presents with rashes appearing on the cheeks, neck, elbow and knee creases, as well as the ankles.
Atopic dermatitis is part of a trio of conditions known as the atopic triad, which includes asthma and hay fever. This triad often coexists, meaning individuals with atopic dermatitis may also have asthma and hay fever. While atopic dermatitis can persist into adulthood, it often improves or diminishes in severity as individuals grow older.
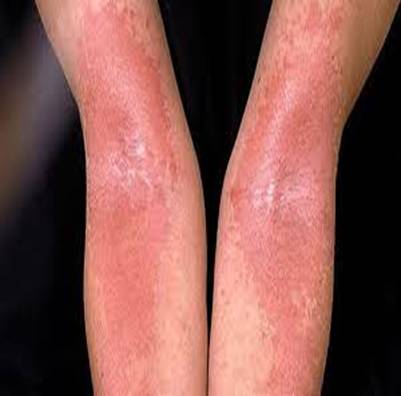
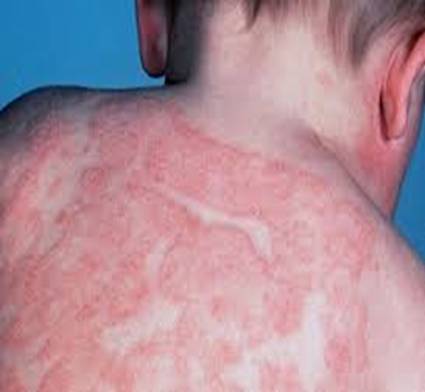
It is important to note that atopic dermatitis varies from person to person, and its management involves personalised approaches tailored to individual needs. Seeking medical advice and support can help individuals navigate the challenges associated with atopic dermatitis and improve their overall well-being.
Sanjivani Homoeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing the condition. By considering individual symptoms, overall health, and underlying imbalances, Sanjivani Homoeopathy aims to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms and restore balance. Natural remedies and personalised treatment plans are utilised to alleviate symptoms, minimise triggers, and improve overall well-being. It is important to consult with a qualified Sanjivani Homoeopathic practitioner for individualised care and support throughout the healing process.
Understanding Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that often begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood. It is characterised by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, which can lead to redness, swelling, and the development of rashes. Eczema can be triggered by various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental allergens, stress, and immune system dysfunction.
Atopic dermatitis, is characterised by the following features:
In atopic dermatitis:
- The rash commonly occurs in the creases of elbows or knees.
- Affected areas of the skin may undergo colour changes, becoming lighter or darker, and may also thicken.
- Itchy small bumps may appear, and if scratched, they can leak fluid.
- Babies often develop the rash on their scalp and cheeks.
- Scratching the skin can lead to infections.
These characteristic symptoms help in identifying and diagnosing atopic dermatitis.
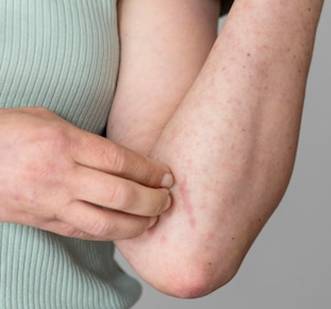
Understanding the Factors and Exploring the Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain genes are associated with an increased risk of developing atopic dermatitis. A family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever can contribute to an individual's susceptibility to the condition.
- Dry Skin: When the skin lacks sufficient moisture, it becomes more prone to irritation and inflammation. Dry skin is a common characteristic of atopic dermatitis and can exacerbate its symptoms.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An underlying immune system dysfunction is thought to play a role in atopic dermatitis. The immune system's abnormal response to certain triggers can lead to inflammation and skin reactions.
- Environmental Triggers: Various environmental factors can trigger or worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms. These triggers may include allergens such as dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and certain foods. Other environmental factors like harsh soaps, detergents, fragrances, and extreme temperatures can also contribute to flare-ups. It is important to note that the exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not fully understood and can vary from person to person. The interplay between genetic factors, skin barrier dysfunction, immune system abnormalities, and environmental triggers likely contributes to the development and progression of the condition.
Complications of Atopic Dermatitis: Understanding the Risks
- A] Asthma and hay fever.
Eczema sometimes precedes these conditions. More than half of young children with atopic dermatitis develop asthma and hay fever by age 13.


- B] Chronic itchy/ scaly skin.
Neurodermatitis, also known as lichen simplex chronicus, is a chronic skin condition characterised by a localised patch of intensely itchy skin. Scratching the area worsens the itch, leading to a cycle of scratching and increased itching. Over time, the affected skin becomes thickened, discoloured, and leathery.
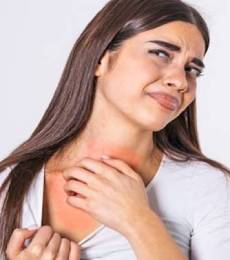
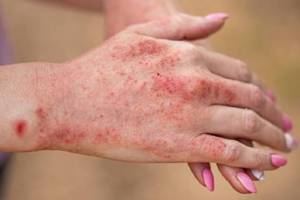
- C] Skin infections Repeated scratching can lead to skin damage, resulting in open sores and cracks. These breaks in the skin increase the vulnerability to infections caused by bacteria and viruses, including the herpes simplex virus. It is important to avoid excessive scratching and take necessary measures to prevent infections in order to manage the condition effectively.
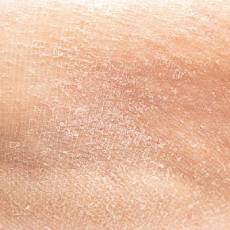
- D] Irritant hand dermatitis. This especially affects people whose work requires that their hands are often wet and exposed to harsh soaps, detergents and disinfectants.
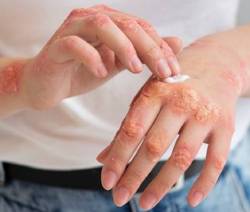
- E] Allergic contact dermatitis. This condition is common in people with atopic dermatitis.
- F] Sleep problems. The itch-scratch cycle can cause poor sleep quality.
2. Contact Dermititis
Complications of Contact Dermatitis: Understanding the Risks
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition characterised by redness, itching, and inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with irritants or allergens.
It comes in two types:
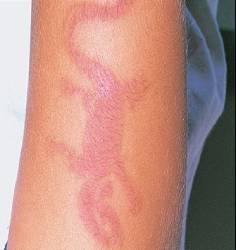
- A] Allergic Contact Dermatitis:
Allergic contact dermatitis is an immune system reaction to an irritant, such as latex or metals. Repeated exposure to an allergen triggers an immune response, leading to dermatitis. Common allergens include metals, fragrances, preservatives, latex, and plants like poison ivy. Symptoms include redness, itching, swelling, and a delayed rash appearing hours or days after exposure.
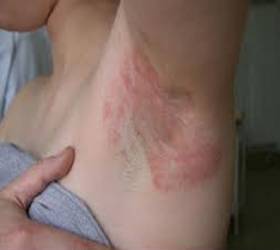
- B] Irritant Contact Dermatitis:
Irritant contact dermatitis is a form of contact dermatitis that occurs when the skin is exposed to irritating substances such as chemicals, detergents, solvents, or acids. This type of dermatitis is commonly seen in individuals who have repeated or prolonged exposure to these substances. It affects the specific area of the skin that comes into direct contact with the irritant and can lead to symptoms like redness, itching, burning, and blistering. Factors such as excessive washing or exposure to toxic substances contribute to the development of irritant contact dermatitis.
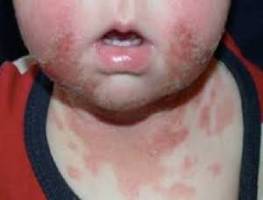
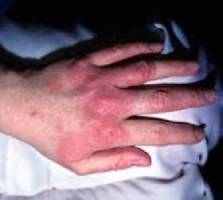
Contact dermatitis presents with a range of symptoms, including:
- Itching, redness, burning, and stinging of the skin
- Formation of itchy bumps known as hives
- Development of fluid-filled blisters that may ooze and crust
- Progressive thickening of the skin, leading to a scaly or leathery texture over time.
Causes of Contact Dermititis
Contact dermatitis happens when you touch a substance that irritates skin or causes an allergic reaction. The most common causes are:

Detergent:
Detergents are widely used substances that can contribute to the development of contact dermatitis.

Friction and Irritation:
Constant rubbing or friction between jewellery and the skin can cause irritation, resulting in redness, itching, and inflammation.

Irritation:
Even in individuals without a latex allergy, repeated or prolonged contact with latex can cause irritation and inflammation of the skin.

Tobacco smoke

Skin care products, including makeup

Soaps and perfumes solvants

Poison ivy and other poisonous plants:
Ivy and other poisonous plants are a result of exposure to specific plant compounds called urushiol. When these plants come into contact with the skin, urushiol is released and can penetrate the skin's surface. Urushiol binds to skin proteins, triggering an immune response in susceptible individuals.

Nickel:
Nickel can cause contact dermatitis by sensitising the immune system through skin exposure. When nickel comes into contact with the skin, it can bind to proteins, forming a complex that triggers an allergic reaction. This reaction leads to the release of inflammatory substances, causing symptoms such as redness, itching, and swelling. The rash typically appears at the site of contact within hours or days after exposure. Common sources of nickel exposure include jewellery, clothing fasteners, coins, and certain cosmetics.

Paint:
Paint can cause contact dermatitis through various mechanisms. Firstly, certain chemicals in paint, such as solvents and pigments, can penetrate the skin and trigger an immune response. This immune reaction can lead to sensitization, making the skin hypersensitive to subsequent exposures. Direct skin contact with wet paint or prolonged contact with dried paint can cause irritation, inflammation, and allergic reactions
Latex Allergic Reaction:
Some individuals develop an allergy to proteins found in natural rubber latex. When latex comes into contact with the skin, it can trigger an immune response, leading to allergic contact dermatitis.
Jewellery Allergenic Metals:
Certain metals used in jewellery, such as nickel, cobalt, and chromium, can trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. Contact with these metals can lead to an immune response and the development of contact dermatitis.
3. Stasis Dermatitis
Introduction of Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis is a skin condition that commonly affects the lower legs and ankles. It is caused by poor blood circulation resulting from venous insufficiency. This condition can lead to a range of uncomfortable symptoms and requires proper management to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications
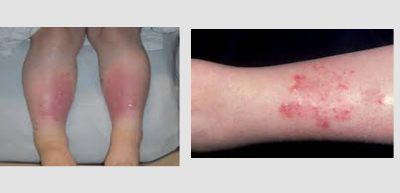
Symptoms of Stasis Dermatitis
The hallmark symptom of stasis dermatitis is a reddish-brown rash, often accompanied by itching, pain, and scaling. The affected skin may appear swollen and feel warm to the touch. Over time, the skin may become thickened, discoloured, and develop open sores or ulcers. In severe cases, complications such as infection and cellulitis can arise. The lower part of legs may swell up, especially during the day when have been walking
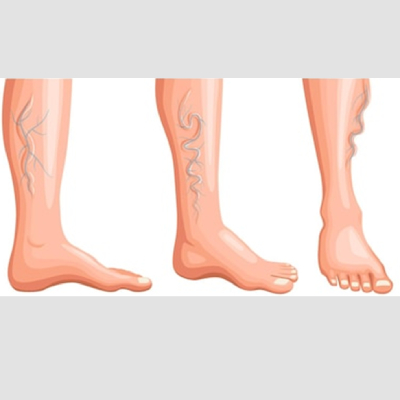
legs may ache or feel heavy
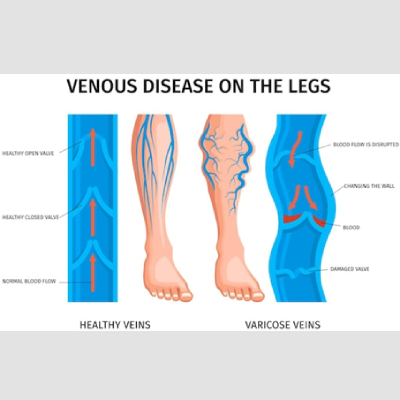
will likely also have varicose veins, which are thick, ropey damaged veins in legs
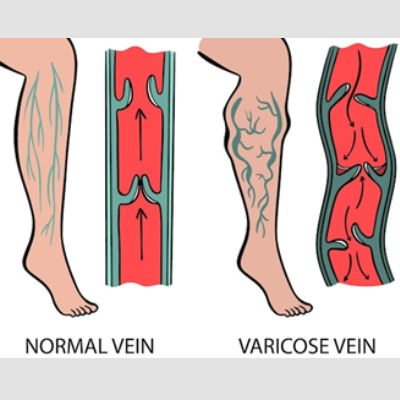
the skin over those varicose veins will be dry and itchy
may develop open sores on your lower legs and on the tops of feet
Causes of Statis Dermititis
Stasis dermatitis is primarily caused by venous insufficiency, which leads to poor blood circulation in the legs. This can result from various factors such as varicose veins, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, pregnancy, and congestive heart failure.
Sanjivani Homoeopathy, can help in managing stasis dermatitis through its holistic approach. Homoeopathic remedies are tailored to individual patients based on their unique symptoms and characteristics.
Sanjivani Homoeopathy aims to address the underlying causes of stasis dermatitis and improve overall blood circulation. It provides personalised treatment plans that focus on stimulating the body's natural healing mechanisms.
Homoeopathic remedies can help alleviate symptoms like itching, pain, swelling, and redness associated with stasis dermatitis. They also aid in reducing inflammation and promoting the healing of the affected skin.
Additionally, Sanjivani Homoeopathy emphasises lifestyle modifications and promotes a healthy lifestyle to complement the treatment. This may include recommendations for regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and elevating the legs to reduce swelling.It is important to consult with a qualified and experienced Sanjivani Homoeopathy practitioner who can assess the individual case and provide appropriate remedies and guidance for stasis dermatitis management.
4. Pompholyx (Dyshidrotic Eczema)
Introduction of Pompholyx(Dyshidrotic Eczema)
Pompholyx, also known as dyshidrotic eczema, is a skin condition characterised by small, itchy blisters that commonly appear on the hands and feet. The exact cause of pompholyx is unknown, but factors such as allergies, stress, and sweating may contribute to its development. Homoeopathy, offered by Sanjivani Homoeopathy, provides a holistic approach to managing pompholyx by addressing underlying imbalances and promoting natural healing.
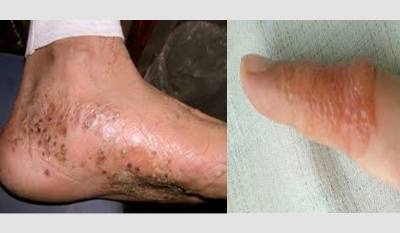
Symptoms of Pompholyx(Dyshidrotic Eczema)
The primary symptom of pompholyx is the formation of small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms, fingers, soles of the feet, or toes. These blisters can be intensely itchy and may cause discomfort or pain. Over time, the blisters may burst, leading to the formation of shallow, moist patches or crusts. In some cases, the affected skin may become red, inflamed, and dry.
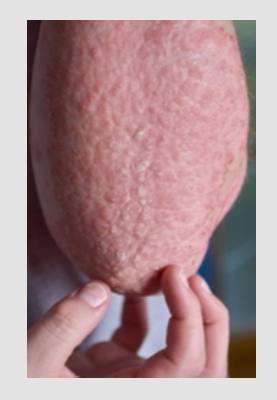
Causes Pompholyx(Dyshidrotic Eczema)
The exact causes of pompholyx are not fully understood. However, it is believed that a combination of factors can contribute to its development. These factors may include allergic reactions to certain substances, excessive sweating, and emotional stress, exposure to irritants like chemicals or metals, and genetic predisposition. Pompholyx is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
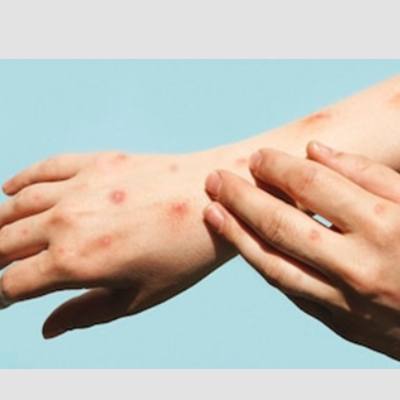
5. Lichen Simplex Chronicus
Introduction of Lichen Simplex Chronicus
Lichen Simplex Chronicus is a chronic skin condition characterised by thickened, itchy patches of skin. It is often a result of repetitive scratching or rubbing of the affected area. This condition can be distressing and challenging to manage, requiring proper understanding of its symptoms and underlying causes.
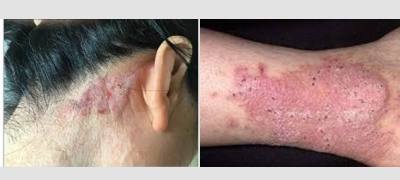
Symptoms of Lichen Simplex Chronicus
The primary symptom of Lichen Simplex Chronicus is the development of thickened, leathery patches of skin that may appear red, scaly, or darker than the surrounding skin. These patches can be intensely itchy and may cause a constant urge to scratch. Over time, the continuous scratching can lead to further thickening and hardening of the affected skin.
Causes of Lichen Simplex Chronicus
Lichen Simplex Chronicus is considered a response to chronic irritation or trauma to the skin. The repetitive scratching or rubbing of the affected area is often triggered by various factors, including:
- Itchy Skin Conditions: Underlying skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or insect bites can cause initial itching, leading to the development of Lichen Simplex Chronicus.
- Emotional Factors:Stress, anxiety, or psychological conditions can contribute to the excessive scratching and rubbing of the skin, worsening the condition.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to certain substances, such as perfumes, soaps, or fabrics, can lead to persistent itching and trigger Lichen Simplex Chronicus.
- Nerve Disorders: Certain nerve disorders, such as peripheral neuropathy or neurodermatitis, can increase sensitivity to itching and result in the development of this condition.
- Behavioural Factors: Habitual scratching or rubbing of the skin due to boredom, anxiety, or obsessive-compulsive tendencies can contribute to the development of Lichen Simplex Chronicus.

6. Nummular Eczema
Introduction of Nummular Eczema
Nmmular eczema, also known as discoid eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by coin-shaped patches of irritated skin. It often presents as itchy, red, and scaly lesions. Understanding the symptoms and underlying causes is crucial for effective management of this condition.
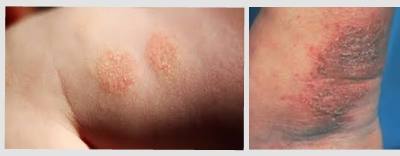
Symptoms of Nummular Eczema
The primary symptom of nummular eczema is the presence of round or oval-shaped patches on the skin. These patches are typically red, dry, and itchy. They may develop a scaly or crusty texture and can be accompanied by pain or a burning sensation. The patches can appear on various parts of the body, but commonly occur on the arms, legs, back, or buttocks.
Causes of Nummular Eczema
The exact causes of nummular eczema are not fully understood. However, certain factors may contribute to its development, including:
- Dry Skin: Individuals with dry skin are more prone to developing nummular eczema, as dryness can compromise the skin barrier and make it more susceptible to irritation.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, fabrics, or allergens can trigger or exacerbate nummular eczema.
- Cold and Dry Weather:Low humidity and cold temperatures can lead to dry skin and trigger nummular eczema flare-ups.
- Skin Injuries: Insect bites, abrasions, or burns can damage the skin, creating an entry point for inflammation and triggering nummular eczema.
- Stress: Emotional stress or anxiety can worsen existing eczema or trigger flare-ups in susceptible individuals.
7 Xerotic (dry skin) Eczema :
Introduction of Xerotic (dry skin) Eczema
Xerotic eczema, also known as dry skin eczema, is a skin condition characterised by excessively dry, flaky, and itchy skin. It occurs when the skin's natural moisture barrier is compromised, leading to increased dryness and sensitivity.
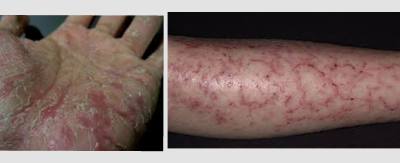
Symptoms of Xerotic (dry skin) Eczema
The main symptom of xerotic eczema is severely dry skin that appears rough, scaly, and may crack or peel. It often causes itching and discomfort. The affected areas are typically localised and can occur on different parts of the body, such as the legs, arms, or trunk.
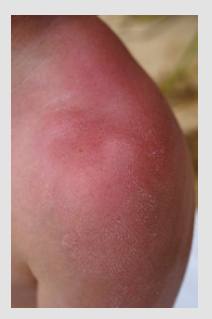
Causes of Xerotic (dry skin) Eczema
Xerotic eczema can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Low Humidity: Dry climates or environments with low humidity levels can contribute to the development of xerotic eczema.
- Ageing: As we age, the skin's natural ability to retain moisture decreases, making older individuals more susceptible to xerotic eczema.
- Harsh Soaps and Cleansers: Using harsh soaps, detergents, or other cleansing products that strip the skin of its natural oils can lead to dryness and eczema.
- Hot Showers or Baths: Frequent hot showers or baths can strip the skin of moisture and exacerbate dryness, contributing to xerotic eczema.
- Winter Season: Cold temperatures and dry indoor heating during the winter season can worsen dryness and trigger xerotic eczema.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing xerotic eczema, with a family history Of dry skin conditions.
8. Seborrheic dermatitis
Introduction of Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas with high oil gland activity, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. It is characterised by red, itchy, and flaky skin patches.
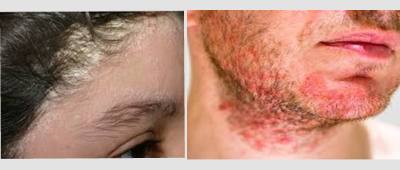
Symptoms of Seborrheic dermatitis
The main symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include redness, itching, and greasy or scaly patches on the affected areas. These patches can range from mild dandruff-like flakes to thick, yellowish crusts. Common areas of involvement are the scalp, eyebrows, sides of the nose, and behind the ears.
Causes of Seborrheic dermatitis
The exact causes of seborrheic dermatitis are not fully understood. However, several factors may contribute to its development, including:
- Malassezia Yeast: An overgrowth of the Malassezia yeast on the skin is thought to play a role in seborrheic dermatitis. This yeast is naturally present on the skin but can cause inflammation and irritation in susceptible individuals.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty or with certain medical conditions, may contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Genetic Predisposition: There appears to be a genetic component to seborrheic dermatitis, as it tends to run in families.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as cold weather, dry air, and stress, can trigger or worsen seborrheic dermatitis.
- Immune System Response: An abnormal immune response to the Malassezia yeast may contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
Eczema Diagnosis
Eczema diagnosis involves a medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests. The process includes:
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about your symptoms, their duration, and any triggers or factors that worsen or alleviate them. They will also inquire about personal or family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will examine your skin, looking for signs of eczema such as redness, itching, dryness, scaling, and rash. They may also check for any other skin conditions or infections.
- Visual Assessment: The appearance and distribution of the rash, along with the presence of characteristic features like flexural involvement or lichenification, help in diagnosing eczema.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: The doctor will rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as psoriasis, contact dermatitis, or fungal infections, through clinical evaluation and, if necessary, additional tests.
- Allergy Testing (if indicated): In cases where there is a suspected association with allergies, specific allergy tests like skin prick tests or blood tests may be performed to identify potential allergens.
Diagnosing eczema involves a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional or dermatologist to differentiate it from other skin conditions. This ensures appropriate treatment and management plans tailored to individual needs.
Homoeopathy and Eczema
Homoeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing eczema by addressing the underlying causes, reducing inflammation, relieving itching, and promoting overall skin health. Homoeopathic remedies are selected based on an individual's specific symptoms, skin presentation, and constitutional factors. The goal of homoeopathy is to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms, restore balance, and improve the overall health of the skin.
Homoeopathic Medication for Eczema
Here are the key characteristics, indications, and symptoms of various homoeopathic remedies commonly used for eczema:
- Arsenicum album:
- Anxiety and restlessness
- Dry, itchy, and burning skin
- Itching worsens with scratching, relieved by heat
- Indigestion with burning pain and feeling of chilliness
- Calcarea carbonica:
- Chilly with clammy hands and feet
- Eczema and cracking skin worsen in winter
- Easily fatigued, anxious, and overwhelmed
- Cravings for sweets and eggs, sluggish metabolism, and weight problems
- Graphites:
- Tough or leathery skin with cracks and soreness
- History of skin disorders
- Cracked areas with golden oozing discharge that forms crusts
- Itching worsens from getting warm in bed, scratching leads to bleeding
- Hepar sulphuris calcareum:
- Very sensitive and chilly individuals
- Extremely sore eczema prone to infection
- Chapped and deeply cracked skin on hands and feet
- Low resistance to illness and infection
- Mezereum:
- Strong anxiety felt in the stomach
- Intensely itching eruptions with blisters and thick crusts
- Itch relieved by cold applications, person is generally chilly
- Craving for fat, feels better in open air
- Rhus toxicodendron:
- Blister-like eruptions that are red, swollen, and intensely itchy
- Soothed by hot applications
- Restless, irritable, and anxious
- Muscle stiffness relieved by warmth and motion, craves cold milk
- Sulphur:
- Burning, itching, and inflamed eruptions worsened by warmth and bathing
- Red, scaling, or crusted skin
- Dry or moist eruptions
- Previous unsuccessful use of medications and ointments
- Antimonium crudum:
- Thick, cracked skin with eczema
- Prone to indigestion
- Sensitive, sentimental, and love to eat
- Itching worsens with warmth and sun exposure
- Arum triphyllum:
- Allergic skin eruptions focused on the lower part of the face, especially around the mouth
- Chapped chin, hot, and irritated
- Cracked and raw lips from picking
- Tendency toward throat irritation and hoarseness
- Calendula:
- Potentized homoeopathic form can be helpful for infected irritated skin
- Topical use of non potentized herb soothes inflammation and prevents infection without suppressing it
- Petroleum:
- Extremely dry skin prone to cracking, especially fingertips and palms
- Eczema worsens in winter, with deep, sore cracks that may bleed
- Cold sensation after scratching
- Easily infected skin, may become tough and leathery from chronic irritation
Benefits of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Individualised Care: Homoeopathy recognizes that each person's experience with eczema is unique. A homoeopath will assess the symptoms, medical history, and individual characteristics to prescribe a personalised treatment plan tailored to the individual's needs.
- Symptom Relief: Homoeopathic remedies aim to relieve itching, reduce inflammation, and promote the healing of skin rashes associated with eczema. They provide natural support without the potential side effects of long-term medication use.
- Improved Skin Health: Homoeopathy focuses on strengthening the skin's natural defences, enhancing the skin barrier function, and promoting overall skin health. This can help prevent future flare-ups and maintain long-term skin well-being.
- Holistic Approach: Homoeopathy considers not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and mental well-being of an individual. It aims to restore balance at all levels, providing comprehensive care.
Patient Review
Consulting a Homeopath
If you are seeking homoeopathic treatment for eczema, it is essential to consult with a qualified and experienced homoeopath. At Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic, our team of skilled homoeopaths will conduct a thorough evaluation, considering your symptoms, medical history, and individual characteristics to develop a personalised treatment plan.
Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic USP
- No homoeopathy Dietary Restrictions:
Allows patients to enjoy foods like onion, garlic, and coffee, ensuring a stress-free treatment journey.
- 24/7 Online Consultations:
Enables convenient access to doctors with detailed counseling, history management, and follow-ups.
- Highly Skilled Team:
Experienced BHMS and MD doctors, supported by multilingual and professional staff.
- Patient-Centric Care:
Simplifies treatment with modern, adaptable solutions and clear communication.
Click Here for Detailed "Sanjivani USP"
FAQ's
- What is homoeopathy ?
Homoeopathy is a holistic science which belives in the law of Similia Similibus Curenter i.e Like Cures Like .It was discovered by Dr Samuel Christian Hahnemannn in 1796.
- Is there any side effects of homoeopathy?
As homoeopathic medicines are made from natural substances this medicines have no side effects and are completely safe to consume
- Is there any diet restriction to take homoeopathic medicines?
There are no diet restrictions for homoeopathic medicines. One should only avoid eating or drinking any liquid other than water at least 30 minutes before and after taking homoeopathic medicines.
Click Here for "Frequently Asked Questions."
Conclusion
Eczema can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the holistic approach of homoeopathy, there is hope for natural support, symptom relief, and improved skin health. Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic is dedicated to providing personalised and effective treatments for eczema. Contact us today to embark on a journey toward managing your symptoms and enhancing your overall well-being.
Disclaimer :The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any treatment for Eczema or any other medical condition.


