Introduction
A burn is a type of injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. While rates are similar for males and females the underlying causes often differ. Among women in some areas, risk is related to use of open cooking fires or unsafe cook stoves. Among men, risk is related to the work environment. Alcoholism and smoking are other risk factors. Burns can also occur as a result of self-harm or violence between people
Understanding Burn
Burns are one of the most common household injuries, especially among children. The term “burn” means more than the burning sensation associated with this injury. Burns are characterised by severe skin damage that causes the affected skin cells to die.
Types of Burns
There are three primary types of burns :
- First Degree
- Second Degree
- Third Degree
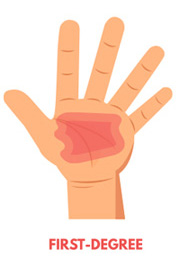
First-Degree Burn
First-degree burns cause minimal skin damage. They are also called “superficial burns” because they affect the outermost layer of skin.
Signs of a first-degree burn include
- Redness
- Minor inflammation, or swelling
- Pain
- Dry, peeling skin occurs as the burn heals
Since this burn affects the top layer of skin, the signs and symptoms disappear once the skin cells shed. First-degree burns usually heal within 7 to 10 days without scarring if the burn affects a large area of skin, more than three inches, and if it’s on your face or a major joint, which include-
- Knee
- Ankle
- Foot
- Spine
- Shoulder
- Elbow
- Forearm
First-degree burns are usually treated with Home care. Healing time may be quicker the sooner you treat the burn.
Treatments for a first-degree burn include:
Soaking the wound in cool water for five minutes or longer. Make sure you don’t use ice, as this may make the damage worse. Never apply cotton balls to a burn because the small fibres can stick to the injury and increase the risk of infection. Also, avoid home remedies like butter and eggs as these are not proven to be effective.
Second-Degree Burn
Second-degree burns are more serious because the damage extends beyond the top layer of skin. This type of burn causes the skin to blister and become extremely red and sore.
Some blisters pop open, giving the burn a wet or weeping appearance. Over time, thick, soft, scab-like tissue called fibrinous exudate may develop over the wound.
Due to the delicate nature of these wounds, keeping the area clean and bandaging it properly is required to prevent infection. This also helps the burn heal quicker.

Some second-degree burns take longer than three weeks to heal, but most heal within two to three weeks without scarring, but often with pigment changes to the skin.
The worse the blisters are, the longer the burn will take to heal. In some severe cases, skin grafting is required to fix the damage. Skin grafting takes healthy skin from another area of the body and moves it to the site of the burned skin.
As with first-degree burns, avoid cotton balls and questionable home remedies. Treatments for a mild second-degree burn generally include:
Running the skin under cool water for 15 minutes or longer However, seek emergency medical treatment if the burn affects a widespread area, such as any of the following:
- Face
- Hands
- Buttocks
- Groin
- Feet
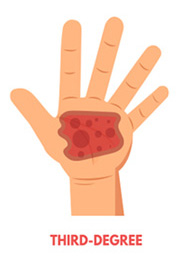
Third-Degree Burn
Excluding fourth-degree burns, third-degree burns are the most severe. They cause the most damage, extending through every layer of skin. There is a misconception that third-degree burns are the most painful. However, with this type of burn the damage is so extensive that there may not be any pain because of nerve damage.
Depending on the cause, the symptoms third-degree burns can exhibit include:
- Waxy and white colour
- Char
- Dark brown colour
- Raised and leathery texture
- Blisters that do not develop
Without surgery, these wounds heal with severe scarring and contracture. There is no set timeline for complete spontaneous healing for third-degree burns.
Causes
Burns are caused by :
- Fire
- Hot liquid or steam
- Hot metal, glass or other objects
- Electrical currents
- Radiation, such as that from X-rays
- Sunlight or other sources of ultraviolet radiation, such as a tanning bed
- Chemicals such as strong acids, lye, paint thinner or gasoline
- Abuse

Complication
Complications of deep or widespread burns can include :
- Bacterial infection, which may lead to a bloodstream infection (sepsis)
- Fluid loss, including low blood volume (hypovolemia)
- Dangerously low body temperature (hypothermia)
- Breathing problems from the intake of hot air or smoke
- Scars or ridged areas caused by an overgrowth of scar tissue (keloids)
- Bone and joint problems, such as when scar tissue causes the shortening and tightening of skin, muscles or tendons (contractures)
Third-degree burns that are deep and affect a large portion of skin are very serious and can be life-threatening. Even first- and second-degree burns can become infected and cause discoloration and scarring. First-degree burns don’t cause scarring.
Potential complications of third-degree burns include -
- Arrhythmia, or heart rhythm disturbances, caused by an electrical burn
- Dehydration
- Disfiguring scars and contractures Edema (excess fluid and swelling in tissues)
- Organ failure
- Pneumonia
- Seriously low blood pressure (hypotension) that may lead to shock.
- Severe infection that may lead to amputation or sepsis
Prevention
The obvious best way to fight burns is to prevent them from happening. Certain jobs put you at a greater risk for burns, but the fact is that most burns happen at home. Infants and young children are the most vulnerable to burns. Preventive measures can take at home include :
- Keep children out of the kitchen while cooking.
- Turn pot handles toward the back of the stove.
- Place a fire extinguisher in or near the kitchen.
- Test smoke detectors once a month.
- Replace smoke detectors every 10 years.
- Keep the water heater temperature under 120 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Measure bath water temperature before use.
- Lock up matches and lighters.
- Install electrical outlet covers.
- Check and discard electrical cords with exposed wires.
- Keep chemicals out of reach, and wear gloves during chemical use.
- Wear sunscreen every day, and avoid peak sunlight.
- Ensure all smoking products are stubbed out completely.
- Clean out dryer lint traps regularly.

Diagnosis
If you go to a doctor for burn treatment, he or she will assess the severity of your burn by examining skin. He or she may recommend that you be transferred to a burn centre if the burn covers more than 10 percent of your total body surface area, is very deep, is on the face, feet or groin. Doctor will check for other injuries and might order lab tests, X-rays or other diagnostic procedures.
Rule of 9 -
- Head = 9%
- Chest (front) = 9%
- Abdomen (front) = 9%
- Upper/mid/low back and buttocks = 18%
- Each arm = 9%
- Each palm = 1%
- Groin = 1%
- Each leg = 18% total (front = 9%, back = 9%)
As an example, if both legs (18% x 2 = 36%), the groin (1%) and the front chest and abdomen were burned, this would involve 55% of the body.
Homoeopathy and Burn
- Aconite
Use immediately after the accident to counteract the nervous shock or when reaction has taken place, and there is dry, burning heat of the skin, heat hot and painful, face is red, pulse hard, frequent and contracts. There is great restlessness, panic and fear of death.
- Apis Mellifica
This remedy relieves pink, swollen skin with itching, burning pain improved by applying cold compresses.
- Arnica
Helps prevent sequel, Such as shock after severe, deep burns and prevent septicemia. Inflammation of skin and cellular tissue with extreme tenderness and pain. Patient does not want to approach and tell everyone present they are all right and wants to be left alone.
This is a valuable first-aid remedy to help reduce pain and swelling and prevent the onset of shock after any injury. Another remedy that is more specific to the burn should be considered after Arnica.
- Arsenicum
Deep burns with vesicles and infected flesh that turn black showing tendency towards gangrene, Inflammatory swelling, with burning, lancinating pains. Infection from dead tissue remaining in the wound, great anguish and restlessness, changes place constantly. Fents death and being left above. Thinks it is useless to take medicine. Prostration which may seem out of proportion with the situation is colic after severe burn.
- Calendula
This remedy is useful for minor superficial burns caused by fire or the sun. Calendula also prevents gangrene and promotes granulation as well as prevents disfiguring scars. Prevents loss of blood and excessive pain. It is a good remedy to use to promote healing after specific acute remedies have removed the shock, pain and immediate symptoms. Use this remedy internally in potency and externally as a lotion. This remedy has a slight antiseptic action, speeds up the healing of damaged skin, and keeps the skin moisturised.
- Cantharis
If used early it will prevent the formation of blisters. This is the most used remedy for scalds, burn and sunburns with vesicular character, blisters and superficial ulceration. Small blisters coalesce to form large blisters. Burns and scald with rawness and burning > by cold applications, followed by undue inflammation. Tetanic or epileptiform convulsions followed by coma. Extensive burns cause a renal complication. Patient is < by touch, approach and > rest. Use internally and externally in lotion. If a burn is intensely painful and blisters seem to be forming, this remedy may help to bring relief. The person often feels more sad than restless from the pain. Rawness and soreness may develop in the injured area.
- Carbolic Acid
Useful for the ill effects of deep burns as well as old burns do not get well. Chemical burns and scalds. Intensely sympathetic, thinking of complaints aggravate them.
- Rhus Tox
After burns and scalds with vesicles, bullae (large blisters), Pustules. The burns are extensive burn more superficial although there may be erysipelas with typhoid like symptoms, sensorium becoming cloudy.
- Urtica urens
For simple burns involving the skin, superficial burns. Intense burning and itching. Useful is chemical burns caused by poisonous plants used internally and externally. When a burn is mild and the primary symptoms are redness and stinging pain, this remedy often brings relief. It is often useful for sunburn when the pain is prickly and stinging.
- Causticum
This is a wonderful remedy for burns of a second degree. It will remove the pain and speed the healing of the skin. The sensation of a Causticum state will be burning, rawness and soreness. There can be restlessness and irritability with tearfulness. This remedy is very good for burns that are slow in healing.
- Hypericum
It is wonderful for healing nerve damage that might have occurred with burns, preventing infection and relieving the itch as the skin heals. It can be given alongside the other remedies. It also helps to relieve the pain after skin grafts. This remedy is often helpful when the pain of a burn is intense and the nerves are extremely sensitive. Along with the usual discomfort of a burn, stabbing or shooting pains may be felt in the injured area.
- Thiosinaminum
Which is fabulous for dissolving scar tissue as the burns enter their later stage of healing and the skin can become a bit ropey and thick.
- Hepar sulphuris calcareum
This remedy is helpful for treating very sensitive and painful burns in people who are prone to infection. The person may feel extremely vulnerable and irritable, and may have chills or be very sensitive to cold.
- Phosphorus
This remedy may be useful for the pain of electrical burns, on the way to medical care. (When electrical burns occur, the damaged area may look small on the surface, but be more extensive underneath; they should always be examined by a doctor.
- Calendula and Hypericum tinctures
These tinctures (used topically in unpotentized herbal form) often are helpful in soothing burns and promoting tissue healing.
Benefits of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Individualised Care: Homoeopathy recognizes that each person's experience with eczema is unique. A homoeopath will assess the symptoms, medical history, and individual characteristics to prescribe a personalised treatment plan tailored to the individual's needs.
- Symptom Relief: Homoeopathic remedies aim to relieve itching, reduce inflammation, and promote the healing of skin rashes associated with eczema. They provide natural support without the potential side effects of long-term medication use.
- Improved Skin Health: Homoeopathy focuses on strengthening the skin's natural defences, enhancing the skin barrier function, and promoting overall skin health.
- Holistic Approach: Homoeopathy considers not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and mental well-being of an individual. It aims to restore balance at all levels, providing comprehensive care.
Consulting a Homeopath
When treating burns, it is essential to consult a homoeopath, especially for severe burns. A Sanjivani homoeopath can provide a comprehensive treatment plan that includes specific remedies tailored to the type and severity of the burn. They can also monitor the healing process and adjust treatments as necessary. Consulting a Sanjivani homoeopath ensures that the treatment is holistic, addressing not just the physical symptoms but also the emotional and psychological impact of the injury.
Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic USP
- No homoeopathy Dietary Restrictions:
Allows patients to enjoy foods like onion, garlic, and coffee, ensuring a stress-free treatment journey.
- 24/7 Online Consultations:
Enables convenient access to doctors with detailed counseling, history management, and follow-ups.
- Highly Skilled Team:
Experienced BHMS and MD doctors, supported by multilingual and professional staff.
- Patient-Centric Care:
Simplifies treatment with modern, adaptable solutions and clear communication.
Click Here for Detailed "Sanjivani USP"
FAQ's
- What is homoeopathy ?
Homoeopathy is a holistic science which belives in the law of Similia Similibus Curenter i.e Like Cures Like .It was discovered by Dr Samuel Christian Hahnemannn in 1796.
- Is there any side effects of homoeopathy?
As homoeopathic medicines are made from natural substances this medicines have no side effects and are completely safe to consume
- Is there any diet restriction to take homoeopathic medicines?
There are no diet restrictions for homoeopathic medicines. One should only avoid eating or drinking any liquid other than water at least 30 minutes before and after taking homoeopathic medicines.
Click Here for "Frequently Asked Questions."
Conclusion
Burns can range from minor to severe and require appropriate treatment to promote healing and prevent complications. Homoeopathy offers a range of remedies that can effectively treat burns, alleviate pain, and accelerate healing. For severe burns, it is crucial to consult a Sanjivani homoeopath to ensure proper care and management. Preventive measures at home can also significantly reduce the risk of burns, particularly for vulnerable populations like infants and young children. By understanding the types of burns and the available homoeopathic treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to manage burns and support better healing.
Disclaimer : The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any treatment for Burn or any other medical condition.


