Introduction
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disorder that results in unpredictable hair loss. For most people, hair falls out in small patches about the size of a quarter. While this hair loss is often limited to a few patches, it can be more extreme in some cases, leading to complete loss of hair on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or even the entire body (alopecia universalis). This condition can affect individuals of any age and gender, though it most commonly occurs before the age of 30.

Understanding Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is characterised by the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to hair loss. This autoimmune response causes hair to fall out in small, round patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. The extent and severity of hair loss can vary widely among individuals. Some may experience only a few small patches, while others may lose all hair on their scalp or body. The condition is unpredictable, and hair loss and regrowth can occur in cycles.
Causes of Alopecia Areata
- Autoimmune Response: The primary cause of alopecia areata is an autoimmune reaction where the immune system attacks the hair follicles.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of alopecia areata or other autoimmune disorders can increase the risk.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menopause, and after childbirth can trigger alopecia areata.
- Psychological Factors: Conditions like trichotillomania, where individuals compulsively pull out their hair, can lead to hair loss.
- Fungal Infections:Scalp infections like seborrheic dermatitis and tinea capitis can cause temporary hair loss.
- Mechanical Factors:Tight hairstyles causing traction alopecia can contribute to hair loss.
- Chemical Exposure: Long-term use of certain hair products can damage hair follicles, leading to alopecia.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
- Patchy Hair Loss : The primary symptom is hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp or other body parts.
- Exclamation Mark Hairs: Short, broken hairs at the edges of bald patches resembling exclamation marks.
- Irritation: Some individuals may experience itching or discomfort in the affected areas.
- Scarring: In some cases, particularly with associated skin conditions, permanent scarring and hair loss can occur.
- Nail Changes: Pitting or other changes in the nails can accompany alopecia areata
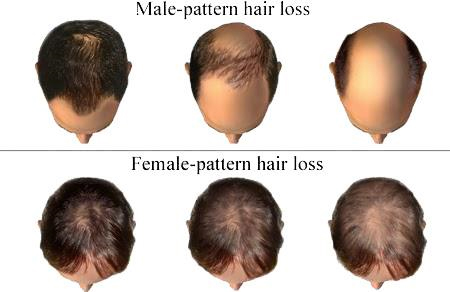
- Alopecia areata in males
- Alopecia areata occurs in both men and women, but the loss of hair is likely to be more significant in men. Men are also more likely to have a family history of the hair loss condition.
- Men may experience hair loss in their facial hair, as well as their scalp, chest, and back hair. Compared to male-pattern baldness, which is a gradual thinning of hair all over, hair loss from this condition causes patchy hair loss.
- Alopecia areata in females
- Females are more likely to develop alopecia areata than males. The hair loss can occur on the scalp, as well as the eyebrows and lashes.
- Unlike female-pattern hair loss, which is a gradual thinning of hair that covers a large area, alopecia areata may be confined to a small area. Hair loss may occur all at once, too. The area can gradually expand, which results in greater hair loss.
- Alopecia areata in children
- Children can develop alopecia areata. While there is some hereditary component to alopecia areata, parents with the condition don’t always pass it on to a child. Likewise, children with this type of hair loss may not have a parent who has it.
- In addition to the hair loss, children may experience nail defects, such as pitting or lesions.
Types of Alopecia Areata
Several types of alopecia areata exist.
Each type is characterised by the extent of hair loss and other symptoms you may be experiencing. Each type may also have a slightly different treatment and prognosis.
- Alopecia areata (patchy)
The main characteristic of this type of alopecia areata is one or more coin-sized patches of hair loss on the skin or body. If this condition expands, it may become alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis.
- Alopecia totalis
Alopecia totalis occurs when you have hair loss across the entire scalp. In this variety, there is a loss of hair over the whole scalp
- Alopecia universalis
In addition to losing hair on the scalp, people with this type of alopecia areata also lose all hair on the face — eyebrows and eyelashes. In alopecia universalis, a complete hair loss occurs all over the body including the beard, armpits, and the private parts.
- Diffuse alopecia areata
Diffuse alopecia areata may look a lot like female or male pattern hair loss. It results in sudden and unexpected thinning of hair all over the scalp, not in just one area or patch.
- Traction Alopecia
Baldness is caused due to the constant mechanical pulling of the hair. This is a reversible condition if treated early, but it may become irreversible in the later stages.
- Ophiasis alopecia
Hair loss that follows a band along the sides and lower back of the scalp is called ophiasis alopecia.
Diagnosis of Alopecia Areata
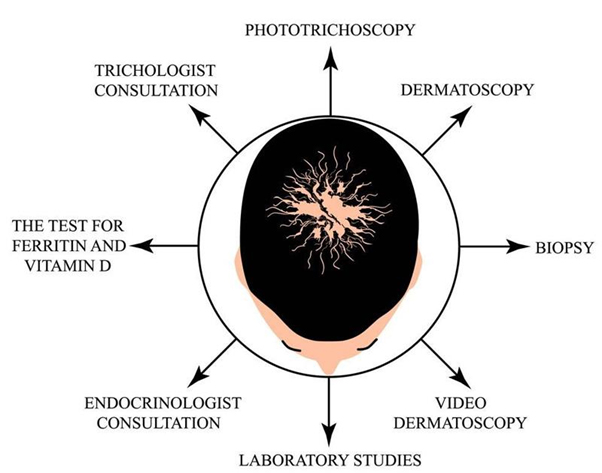
- May be able to diagnose alopecia areata simply by looking at the extent of your hair loss and by examining a few hair samples under a microscope. May also perform a scalp biopsy to rule out other conditions that cause hair loss, including fungal infections like tinea capitis. During a scalp biopsy, will remove a small piece of skin on your scalp for analysis.
- Blood tests might be done if other autoimmune conditions are suspected.
- The specific blood test performed depends on the particular disorder the doctor suspects. However, It will likely test for the presence of one or more abnormal antibodies. If these antibodies are found in your blood, it usually means that you have an autoimmune disorder.
Other blood tests that can help rule out other conditions include the following:
- C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Iron levels
- Antinuclear antibody test
- Thyroid hormones
- Free and total testosterone
- Follicle stimulating and luteinizing hormone
Diet of Alopecia Areata
- Foods with sugar, processed snacks, and alcohol may increase inflammation and irritation within the body.
- Some individuals with a diagnosed autoimmune condition may consider following an “anti-inflammatory” diet. This type of eating plan is designed to help reduce the autoimmune response in the body and decrease the chances of another hair loss episode or further hair loss.
- To do that, you eat foods that are known to ease the inflammation process. The foundational foods of this diet, also known as the autoimmune protocol, are fruits and vegetables like blueberries, nuts, seeds, broccoli, beets, and lean meats like wild-caught salmon.
- Eating a balanced diet — one with whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean meat — is beneficial to your overall health for many reasons, not just for reducing inflammation.
Homoeopathic medicines for Alopecia Areata
- Fluoric acid
- Tendency to develop alopecia in families.
- Brittle hair.
- Idiopathic hair fall.
- Hair falls in spots, vertex baldness.
- Hair tangles easily.
- Light hearted attitude towards life.
- Extreme irritability and anger.
- All complaints aggravated by warmth and better by cold application.
- Phosphoric acid
- Any sort of grief leading to hair fall
- Takes stress easily
- Early greying of hair (sometimes in childhood)
- Progressive thinning of hair
- Difficult comprehension of things
- Long-standing effects of mental agony and patient lives in the state of shock for long
- Extreme debility
- Craves juicy things
- Phosphorus
- Patchy baldness
- Dryness of hair and scalp, itchy scalp, dandruff
- Hair fall in handfuls while combing
- Frontal baldness
- Thin physique, long fingers, high cheekbones
- Weakness with excess emotional vulnerability and impressionability
- Extremely sympathetic persons who go out-of-the-way to help others
- Hair fall after any hemorrhagic disorder
- Scurvy
- Fearful when alone
- Better in company
- Graphites
- Hair fall on sides
- Patchy baldness
- Itchy, humid eruptions on scalp that emit foetid odour
- Constipation associated with hair fall
- Chilly, fat patient with tendency to develop one or the other skin problems
- Menopausal hair fall
- Mezereum
- Hair stick together
- Fall in handfuls
- Crusty eruptions on scalp leading to hair fall
- Itchy scalp, dandruff
- Alopecia Areata affecting scalp leading to hair fall
- Sensitive to cold air, skin rashes, eruptions, crusts below which is yellow purulent matter.
- Sepia
- Baldness menopausal
- Hair fall after delivery of the child with mental depression, leading to indifference later on
- Hair pains when touched because of extremely sensitive hair roots
- Irritability increased, with snappish attitude
- Pimply eruptions near the hairline on forehead
- Silica
- Baldness in young people
- Hair fall in frontal and forehead region
- Early greying of hair
- Chilly with excessively sweaty cold palms
- Nervous and anxious disposition
- Mild types
- Fixed ideas, highly impressionable
- Natrum muriaticum
- It is frequently prescribed in cases of hair loss especially in anaemic females.
- Lycopodium
- This drug is frequently prescribed for complaints of hair loss, premature baldness, premature greying of hair.Offensive secretions and violent itching are a few of its common indications. The complaints are worse from warmth and better by cold applications.
- Nitricum acidum
- Its one of the commonly used drugs for hair loss.
- Loss of hair from the vertex. Sensitiveness of the scalp.
Benefits of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Individualised Care: Homoeopathy recognizes that each person is unique. A homoeopath will assess your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle to prescribe a personalised treatment plan tailored to your needs.
- Gentle and Natural: Homoeopathic remedies are derived from natural substances and are known for their minimal side effects. They work in harmony with the body, promoting self-healing and overall well-being.
- Holistic Approach: Homoeopathy takes into account not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and mental aspects of an individual. It aims to restore balance at all levels, providing comprehensive care.
- Long-Term Relief: By addressing the underlying causes of lumbar spondylosis, homoeopathy strives to achieve long-term relief and improved quality of life.
Consulting a Homeopath
If you are seeking homoeopathic treatment for lumbar spondylosis, it is essential to consult with a qualified and experienced homoeopath. At Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic, our team of skilled homoeopaths will conduct a thorough evaluation, considering your symptoms, medical history, and individual characteristics to develop a personalised treatment plan.
Sanjivani Homeopathy Clinic USP
- No homoeopathy Dietary Restrictions:
Allows patients to enjoy foods like onion, garlic, and coffee, ensuring a stress-free treatment journey.
- 24/7 Online Consultations:
Enables convenient access to doctors with detailed counseling, history management, and follow-ups.
- Highly Skilled Team:
Experienced BHMS and MD doctors, supported by multilingual and professional staff.
- Patient-Centric Care:
Simplifies treatment with modern, adaptable solutions and clear communication.
Click Here for Detailed "Sanjivani USP"
FAQ's
- What is homoeopathy ?
Homoeopathy is a holistic science which belives in the law of Similia Similibus Curenter i.e Like Cures Like .It was discovered by Dr Samuel Christian Hahnemannn in 1796.
- Is there any side effects of homoeopathy?
As homoeopathic medicines are made from natural substances this medicines have no side effects and are completely safe to consume
- Is there any diet restriction to take homoeopathic medicines?
There are no diet restrictions for homoeopathic medicines. One should only avoid eating or drinking any liquid other than water at least 30 minutes before and after taking homoeopathic medicines.
Click Here for "Frequently Asked Questions."
Conclusion
Alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune disorder that can lead to significant hair loss. Understanding its causes and symptoms is crucial for effective management. Homoeopathy provides a natural and holistic approach to treating alopecia areata, offering personalised remedies to address the root causes and symptoms. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable treatment. Sanjivani Homoeopathy can be a valuable option for those seeking natural relief from the effects of alopecia areata.
Disclaimer : The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any treatment for alopecia areata or any other medical condition.


